Expression of pro- and anti-angiogenic factors during the formation of the periocular vasculature and development of the avian cornea
- PMID: 23444323
- PMCID: PMC3671393
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.23956
Expression of pro- and anti-angiogenic factors during the formation of the periocular vasculature and development of the avian cornea
Abstract
Background: During embryonic development, endothelial precursor cells (angioblasts) migrate relatively long distances to form the primary vascular plexus. The migratory behavior of angioblasts and localization of the primitive blood vessels is tightly regulated by pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors encountered in the embryonic environment. Despite the importance of corneal avascularity to proper vision, it is not known when avascularity is established in the developing cornea and how pro- and anti-angiogenic factors regulate this process.
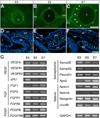
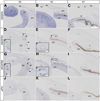
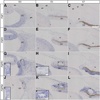
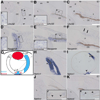
Results and discussion: Using Tg(tie1:H2B:eYFP) transgenic quail embryos to visualize fluorescently labeled angioblasts, we show that the presumptive cornea remains avascular despite the invasion of cells from the periocular region where migratory angioblasts reside and form the primary vasculature. Semiquantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction analysis and spatiotemporal examination of gene expression revealed that pro- and anti-angiogenic factors were expressed in patterns indicating their potential roles in angioblast guidance.
Conclusions: Our findings show for the first time that chick corneal avascularity is established and maintained during development as the periocular vasculature forms. We also identify potential candidate pro- and anti-angiogenic factors that may play crucial roles during vascular patterning in the anterior eye.
Copyright © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sema3A maintains corneal avascularity during development by inhibiting Vegf induced angioblast migration.Dev Biol. 2014 Jul 15;391(2):241-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.04.017. Epub 2014 May 6. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24809797 Free PMC article.
-
PlexinD1 is required for proper patterning of the periocular vascular network and for the establishment of corneal avascularity during avian ocular development.Dev Biol. 2016 Mar 1;411(1):128-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Jan 16. Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26783882 Free PMC article.
-
Corneal avascularity is due to soluble VEGF receptor-1.Nature. 2006 Oct 26;443(7114):993-7. doi: 10.1038/nature05249. Epub 2006 Oct 18. Nature. 2006. PMID: 17051153 Free PMC article.
-
The role of FGF and VEGF in angioblast induction and migration during vascular development.Dev Dyn. 2001 Jan;220(1):1-17. doi: 10.1002/1097-0177(2000)9999:9999<::AID-DVDY1087>3.0.CO;2-2. Dev Dyn. 2001. PMID: 11146503 Review.
-
Inflammatory corneal neovascularization: etiopathogenesis.Semin Ophthalmol. 2011 Jul-Sep;26(4-5):235-45. doi: 10.3109/08820538.2011.588652. Semin Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 21958169 Review.
Cited by
-
Sema3A maintains corneal avascularity during development by inhibiting Vegf induced angioblast migration.Dev Biol. 2014 Jul 15;391(2):241-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.04.017. Epub 2014 May 6. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24809797 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of CXCL14 disrupts neurovascular patterning during ocular development.Dev Biol. 2017 Mar 1;423(1):77-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.01.008. Epub 2017 Jan 15. Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28095300 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of CXCL12 and CXCL14 during eye development in chick and mouse.Gene Expr Patterns. 2013 Dec;13(8):303-10. doi: 10.1016/j.gep.2013.05.006. Epub 2013 May 30. Gene Expr Patterns. 2013. PMID: 23727298 Free PMC article.
-
PlexinD1 is required for proper patterning of the periocular vascular network and for the establishment of corneal avascularity during avian ocular development.Dev Biol. 2016 Mar 1;411(1):128-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Jan 16. Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26783882 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt Signaling in vascular eye diseases.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2019 May;70:110-133. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2018.11.008. Epub 2018 Dec 1. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 30513356 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams RH, Alitalo K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:464–478. - PubMed
-
- Adler R, Belecky-Adams TL. The role of bone morphogenetic proteins in the differentiation of the ventral optic cup. Development. 2002;129:3161–3171. - PubMed
-
- Aiello LP, Pierce EA, Foley ED, Takagi H, Chen H, Riddle L, Ferrara N, King GL, Smith LE. Suppression of retinal neovascularization in vivo by inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) using soluble VEGF-receptor chimeric proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92:10457–10461. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

