SD-OCT analysis of regional epithelial thickness profiles in keratoconus, postoperative corneal ectasia, and normal eyes
- PMID: 23446013
- PMCID: PMC4123636
- DOI: 10.3928/1081597X-20130129-08
SD-OCT analysis of regional epithelial thickness profiles in keratoconus, postoperative corneal ectasia, and normal eyes
Erratum in
- J Refract Surg. 2013 Apr;29(4):234. Perez-Straziota, E [corrected to Perez-Straziota, Claudia E]
Abstract
Purpose: To assess corneal microarchitecture and regional epithelial thickness profile in eyes with keratoconus, postoperative corneal ectasia (ectasia), and normal unoperated eyes (controls) using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT).
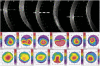
Methods: Regional corneal epithelial thickness profiles were measured with anterior segment SD-OCT (Optovue RTVue-100, Optovue Inc., Fremont, CA). Epithelial thickness was assessed at 21 points, 0.5 mm apart, across the central 6-mm of the corneal apex in the horizontal and vertical meridians.
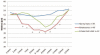
Results: One hundred twenty eyes were evaluated, including 49 eyes from 29 patients with keratoconus, 32 eyes from 16 patients with ectasia, and 39 eyes from 21 control patients. Average epithelial thickness at the corneal apex was 41.18 ± 6.47 μm (range: 30 to 51 μm) for keratoconus, 46.5 ± 6.72 μm for ectasia (range: 34 to 60 μm), and 50.45 ± 3.92 μm for controls (range: 42 to 55 μm). Apical epithelial thickness was significantly thinner in eyes with keratoconus (P < .0001) and ectasia (P = .0007) than in controls. Epithelial thickness ranges in all other areas varied widely for keratoconus (range: 21 to 101 μm) and ectasia (range: 30 to 82 μm) compared to controls (range: 43 to 64) (P = .0063).
Conclusion: SD-OCT demonstrated significant central and regional epithelial thickness profile differences between keratoconus, ectasia, and control eyes, with significant variability and unpredictability in ectatic eyes. This regional irregularity may necessitate direct epithelial thickness measurement for treatments where underlying stromal variations may be clinically relevant, including corneal collagen cross-linking or topography-guided ablations.
Copyright 2013, SLACK Incorporated.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epithelial and stromal remodeling after corneal collagen cross-linking evaluated by spectral-domain OCT.J Refract Surg. 2014 Feb;30(2):122-7. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20140120-08. J Refract Surg. 2014. PMID: 24763478 Clinical Trial.
-
Distinguishing between contact lens warpage and ectasia: Usefulness of optical coherence tomography epithelial thickness mapping.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2017 Jan;43(1):60-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2016.10.019. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2017. PMID: 28317679 Free PMC article.
-
The role of corneal epithelial thickness map in detecting early keratoconus.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2025 Apr;263(4):1035-1044. doi: 10.1007/s00417-024-06682-9. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39535549
-
Utility of regional epithelial thickness measurements in corneal evaluations.Surv Ophthalmol. 2020 Mar-Apr;65(2):187-204. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2019.09.003. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Surv Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 31560871 Review.
-
Early diagnosis of keratoconus using corneal biomechanics and OCT derived technologies.Eye Vis (Lond). 2025 May 12;12(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s40662-025-00435-3. Eye Vis (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40350508 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Distinguishing Highly Asymmetric Keratoconus Eyes Using Combined Scheimpflug and Spectral-Domain OCT Analysis.Ophthalmology. 2018 Dec;125(12):1862-1871. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2018.06.020. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Ophthalmology. 2018. PMID: 30055838 Free PMC article.
-
Corneal Epithelial Mapping Characteristics in Normal Eyes Using Anterior Segment Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022 Mar 2;11(3):6. doi: 10.1167/tvst.11.3.6. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35258560 Free PMC article.
-
Value of corneal epithelial and Bowman's layer vertical thickness profiles generated by UHR-OCT for sub-clinical keratoconus diagnosis.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 11;6:31550. doi: 10.1038/srep31550. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27511620 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Detailed Distribution of Corneal Epithelial Thickness and Correlated Characteristics Measured with SD-OCT in Myopic Eyes.J Ophthalmol. 2017;2017:1018321. doi: 10.1155/2017/1018321. Epub 2017 May 14. J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28607770 Free PMC article.
-
Corneal Epithelial Thickness Profile in Healthy Portuguese Children by High-Definition Optical Coherence Tomography.Clin Ophthalmol. 2021 Feb 24;15:735-743. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S293695. eCollection 2021. Clin Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33658753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raiskup-Wolf F, Hoyer A, Spoerl E, Pillunat LE. Collagen crosslinking with riboflavin and ultraviolet-A light in keratoconus: long-term results. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008;34(5):796–801. - PubMed
-
- Alió JL, Toffaha BT, Piñero DP, Klonowski P, Javaloy J. Cross-linking in progressive keratoconus using an epithelial debridement or intrastromal pocket technique after previous corneal ring segment implantation. J Refract Surg. 2011;27(10):737–743. - PubMed
-
- Greenstein SA, Fry KL, Hersh PS. Corneal topography indices after corneal collagen crosslinking for keratoconus and corneal ectasia: one-year results. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37(7):1282–1290. - PubMed
-
- Kymionis GD, Portaliou DM, Kounis GA, Limnopoulou AN, Kontadakis GA, Grentzelos MA. Simultaneous topography-guided photorefractive keratectomy followed by corneal collagen cross-linking for keratoconus. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011;152(5):748–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

