Differential roles of the C and N termini of Orai1 protein in interacting with stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) for Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ (CRAC) channel activation
- PMID: 23447534
- PMCID: PMC3630893
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.450254
Differential roles of the C and N termini of Orai1 protein in interacting with stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) for Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ (CRAC) channel activation
Abstract
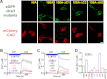
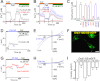
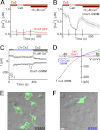
The entry of extracellular Ca(2+), which is mediated by Ca(2+) release-activated Ca(2+) (CRAC) channels, is essential for T cell activation and the normal functioning of other immune cells. Although the molecular components of CRAC channels, the Orai1 pore-forming subunit and the STIM1-activating subunit have been recently identified, the gating mechanism by which Orai1 channels conduct Ca(2+) entry upon Orai1-STIM1 interaction following Ca(2+) store release remains elusive. Herein, we show that C-terminal truncations or point mutations prevented Orai1 from binding to STIM1 and subsequent channel opening. In contrast, an Orai1 mutant with an N-terminal truncation interacted with but failed to be activated by STIM1. Moreover, Orai1 channels with C-terminal disruption, but not N-terminal truncation, could be gated by fused functional domains of STIM1. Interestingly, the channel activities of Orai1 mutants carrying either an N-terminal or a C-terminal truncation were restored by a methionine mutation at the putative gating hinge, the conserved Gly-98 site in the first transmembrane segment (TM1) of Orai1. Collectively, these results support a stepwise gating mechanism of STIM1-operated Orai1 channels; the initial binding between STIM1 and the C terminus of Orai1 docks STIM1 onto the N terminus of Orai1 to initiate conformational changes of the pore-lining TM1 helix of Orai1, leading to the opening of the channel.
Figures







References
-
- Feske S., Müller J. M., Graf D., Kroczek R. A., Dräger R., Niemeyer C., Baeuerle P. A., Peter H. H., Schlesier M. (1996) Severe combined immunodeficiency due to defective binding of the nuclear factor of activated T cells in T lymphocytes of two male siblings. Eur. J. Immunol. 26, 2119–2126 - PubMed
-
- Dolmetsch R. E., Lewis R. S., Goodnow C. C., Healy J. I. (1997) Differential activation of transcription factors induced by Ca2+ response amplitude and duration. Nature 386, 855–858 - PubMed
-
- Feske S., Giltnane J., Dolmetsch R., Staudt L. M., Rao A. (2001) Gene regulation mediated by calcium signals in T lymphocytes. Nat. Immunol. 2, 316–324 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

