Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the endocytosis and surface expression of GluN3A-containing NMDA receptors
- PMID: 23447623
- PMCID: PMC3682218
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2721-12.2013
Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the endocytosis and surface expression of GluN3A-containing NMDA receptors
Abstract
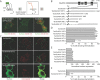
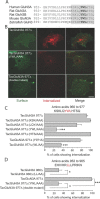
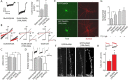
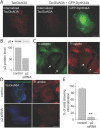
Selective control of receptor trafficking provides a mechanism for remodeling the receptor composition of excitatory synapses, and thus supports synaptic transmission, plasticity, and development. GluN3A (formerly NR3A) is a nonconventional member of the NMDA receptor (NMDAR) subunit family, which endows NMDAR channels with low calcium permeability and reduced magnesium sensitivity compared with NMDARs comprising only GluN1 and GluN2 subunits. Because of these special properties, GluN3A subunits act as a molecular brake to limit the plasticity and maturation of excitatory synapses, pointing toward GluN3A removal as a critical step in the development of neuronal circuitry. However, the molecular signals mediating GluN3A endocytic removal remain unclear. Here we define a novel endocytic motif (YWL), which is located within the cytoplasmic C-terminal tail of GluN3A and mediates its binding to the clathrin adaptor AP2. Alanine mutations within the GluN3A endocytic motif inhibited clathrin-dependent internalization and led to accumulation of GluN3A-containing NMDARs at the cell surface, whereas mimicking phosphorylation of the tyrosine residue promoted internalization and reduced cell-surface expression as shown by immunocytochemical and electrophysiological approaches in recombinant systems and rat neurons in primary culture. We further demonstrate that the tyrosine residue is phosphorylated by Src family kinases, and that Src-activation limits surface GluN3A expression in neurons. Together, our results identify a new molecular signal for GluN3A internalization that couples the functional surface expression of GluN3A-containing receptors to the phosphorylation state of GluN3A subunits, and provides a molecular framework for the regulation of NMDAR subunit composition with implications for synaptic plasticity and neurodevelopment.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
