Design and properties of efficient tRNA:EF-Tu FRET system for studies of ribosomal translation
- PMID: 23447652
- PMCID: PMC3630515
- DOI: 10.1093/protein/gzt006
Design and properties of efficient tRNA:EF-Tu FRET system for studies of ribosomal translation
Abstract
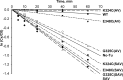
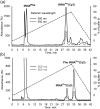
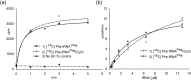
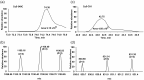
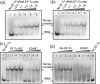
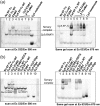
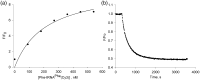
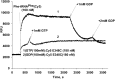
Formation of the ternary complex between GTP-bound form of elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) and aminoacylated transfer RNA (aa-tRNA) is a key event in protein biosynthesis. Here we show that fluorescently modified Escherichia coli EF-Tu carrying three mutations, C137A, C255V and E348C, and fluorescently modified Phe-tRNA(Phe) form functionally active ternary complex that has properties similar to those of the naturally occurring (unmodified) complex. Similarities include the binding and binding rate constants, behavior in gel retardation assay, as well as activities in tRNA protection and in vitro translation assays. Proper labeling of EF-Tu was demonstrated in MALDI mass spectroscopy experiments. To generate the mutant EF-Tu, a series of genetic constructions were performed. Two native cysteine residues in the wild-type EF-Tu at positions 137 and 255 were replaced by Ala and Val, respectively, and an additional cysteine was introduced either in position 324 or 348. The assembly FRET assay showed a 5- to 7-fold increase of Cy5-labeled EF-Tu E348C mutant fluorescence upon formation of ternary complex with charged tRNA(Phe)(Cy3-labeled) when the complex was excited at 532 nm and monitored at 665 nm. In a control experiment, we did not observe FRET using uncharged tRNA(Phe)(Cy3), nor with wild-type EF-Tu preparation that was allowed to react with Cy5 maleimide, nor in the absence of GTP. The results obtained demonstrate that the EF-Tu:tRNA FRET system described can be used for investigations of ribosomal translation in many types of experiments.
Figures
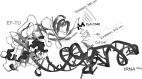



References
-
- Abrahamson J.K., Laue T.M., Miller D.L., Johnson A.E. Biochemistry. 1985;24:692–700. - PubMed
-
- Arai K., Kawakita M., Nakamura S., Ishikawa K., Kaziro Y. J. Biochem. 1974;76:523–534. - PubMed
-
- Berchtold H., Reshetnikova L., Reiser C.O., Schirmer N.K., Sprinzl M., Hilgenfeld R. Nature. 1993;365:126–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

