Impaired TLR5 functionality is associated with survival in melioidosis
- PMID: 23447684
- PMCID: PMC3607401
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202974
Impaired TLR5 functionality is associated with survival in melioidosis
Abstract
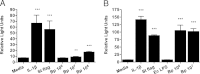
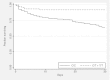
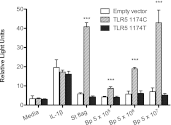
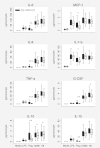
Melioidosis is infection caused by the flagellated saprophyte Burkholderia pseudomallei. TLR5 is a pathogen recognition receptor activated by bacterial flagellin. We studied a genetic variant that encodes a defective TLR5 protein, TLR5(1174C)>T, to elucidate the role of TLR5 in melioidosis. We measured NF-κB activation induced by B. pseudomallei in human embryonic kidney-293 cells transfected with TLR5 and found that B. pseudomallei induced TLR5(1174C)- but not TLR5(1174T)-dependent activation of NF-κB. We tested the association of TLR5(1174C)>T with outcome in 600 Thai subjects with melioidosis. In a dominant model, TLR5(1174C)>T was associated with protection against in-hospital death (adjusted odds ratio: 0.20; 95% confidence interval: 0.08-0.50; p = 0.001) and organ failure (adjusted odds ratio: 0.37; 95% confidence interval: 0.19-0.71; p = 0.003). We analyzed blood cytokine production induced by flagellin or heat-killed B. pseudomallei by TLR5(1174C)>T genotype in healthy subjects. Flagellin induced lower monocyte-normalized levels of IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, IL-10, MCP-1, IL-1ra, G-CSF, and IL-1β in carriers of TLR5(1174T) compared with carriers of TLR5(1174C). B. pseudomallei induced lower monocyte-normalized levels of IL-10 in carriers of TLR5(1174T). We conclude that the hypofunctional genetic variant TLR5(1174C)>T is associated with reduced organ failure and improved survival in melioidosis. This conclusion suggests a deleterious immunoregulatory effect of TLR5 that may be mediated by IL-10 and identifies this receptor as a potential therapeutic target in melioidosis.
Figures
References
-
- Wiersinga W. J., van der Poll T., White N. J., Day N. P., Peacock S. J. 2006. Melioidosis: insights into the pathogenicity of Burkholderia pseudomallei. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4: 272–282 - PubMed
-
- Wiersinga W. J., Wieland C. W., Dessing M. C., Chantratita N., Cheng A. C., Limmathurotsakul D., Chierakul W., Leendertse M., Florquin S., de Vos A. F., et al. 2007. Toll-like receptor 2 impairs host defense in gram-negative sepsis caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei (melioidosis). PLoS Med. 4: e248. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hayashi F., Smith K. D., Ozinsky A., Hawn T. R., Yi E. C., Goodlett D. R., Eng J. K., Akira S., Underhill D. M., Aderem A. 2001. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature 410: 1099–1103 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

