Overexpression and secretion of the soluble CTLA-4 splice variant in various autoimmune diseases and in cases with overlapping autoimmunity
- PMID: 23448385
- PMCID: PMC3609615
- DOI: 10.1089/gtmb.2012.0391
Overexpression and secretion of the soluble CTLA-4 splice variant in various autoimmune diseases and in cases with overlapping autoimmunity
Abstract
Aim: To explore the potential genetic association of CTLA-4 Exon1 +49A/G and 3'UTR (AT)(n) to susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and overlapping (OP) autoimmunity; affected with more than one autoimmune disease. Expression of two major CTLA-4 isoforms; full length (mCTLA-4) and soluble (sCTLA-4) were explored in all subjects. A total of 680-age/gender/ethnically matched Kuwaitis were recruited and polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-fragment analysis was employed for genotyping both markers. mCTLA-4 and sCTLA-4 mRNA expression were analyzed using quantitative real time-PCR. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to screen sCTLA-4 in all subjects' sera.
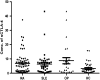
Results: Only two CTLA-4 3'UTR (AT)(n) allelotypes; (AT)(15) and (AT)(6) were detected. The heterozygous (AT)(15/6) genotype confers protectivity rather than susceptibility to SLE (p=0.01, odds ratio=0.43, and confidence interval=0.21-0.86). No significant association was observed between Exon 1 +49A/G and any of the tested diseases. A consistently high serum sCTLA-4 level was observed in RA (6.8 ng/mL, p=0.005), SLE (6.34 ng/mL, p=0.007), and OP (8.75 ng/mL, p=0.012) compared to healthy control. A significant increase in the expression of sCTLA-4 mRNA was observed in OP (p=0.05) and SLE (p=0.047), while a significant increase in the expression of mCTLA-4 (p=0.01) was observed only in OP.
Conclusion: The present study is the first to report a statistically significant association between OP and serum sCTLA-4. The novelty of our study is the significance of CTLA-4 in the pathogenesis of OP besides SLE and RA.
Figures
References
-
- Aguilar F. Torres B. Sanchez-Roman J, et al. CTLA4 polymorphism in Spanish patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Immunol. 2003;64:936–940. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed S. Ihara K. Kanemitsu S, et al. Association of CTLA-4 but not CD28 gene polymorphisms with systemic lupus Erythematosus in the Japanese population. Rheumatol Oxford. 2001;40:662–667. - PubMed
-
- AlFadhli S. Kharrat N. AlRebai A. Genome scan meta- analysis in systemic lupus erythematosus strong linkage with loci 6p22.3-p21.1 and 2q31.1–34. J Med Genet Genomics. 2010;2:001–009.
-
- Anjos S. Nguyen A. Ounissi-Benkalha H, et al. A common autoimmunity predisposing signal peptide variant of the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4. J BiolChem. 2002;277:46478–46486. - PubMed
-
- Ban Y. Davies TF. Greenberg DA, et al. Analysis of the CTLA-4, CD-28, and inducible co-stimulatory (ICOS) gene in thyroid diseases. Genes Immun. 2003;4:586–593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

