Quantifying the effects of social influence
- PMID: 23449043
- PMCID: PMC3584930
- DOI: 10.1038/srep01360
Quantifying the effects of social influence
Abstract
How do humans respond to indirect social influence when making decisions? We analysed an experiment where subjects had to guess the answer to factual questions, having only aggregated information about the answers of others. While the response of humans to aggregated information is a widely observed phenomenon, it has not been investigated quantitatively, in a controlled setting. We found that the adjustment of individual guesses depends linearly on the distance to the mean of all guesses. This is a remarkable, and yet surprisingly simple regularity. It holds across all questions analysed, even though the correct answers differ by several orders of magnitude. Our finding supports the assumption that individual diversity does not affect the response to indirect social influence. We argue that the nature of the response crucially changes with the level of information aggregation. This insight contributes to the empirical foundation of models for collective decisions under social influence.
Figures
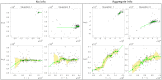

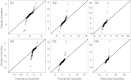
References
-
- Kahan D. M. Social influence, social meaning, and deterrence. Virginia Law Review 83, 349–395 (1997).
-
- Mutz D. Impersonal influence: effects of representations of public opinion on political attitudes. Political Behavior 14, 89–122 (1992).
-
- Helbing D., Farkas I. & Vicsek T. Simulating dynamical features of escape panic. Nature 407, 487–90 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Hirshleifer D. & Teoh S. H. Herd behaviour and cascading in capital markets: a review and synthesis. European Financial Management 9, 25–66 (2003).
-
- Salganik M. J., Dodds P. S. & Watts D. J. Experimental study of inequality and unpredictability in an artificial cultural market. Science 311, 854–856 (2006). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

