Self-regulation in a minimal model of chemical self-replication
- PMID: 23449095
- PMCID: PMC3326146
- DOI: 10.1007/s10867-011-9252-6
Self-regulation in a minimal model of chemical self-replication
Abstract
In biological systems, regulation plays an important role in keeping metabolite concentrations within physiological ranges. To study the dynamical implications of self-regulation, we consider a functional form used in genetic networks and couple it to a mechanism associated with chemical self-replication. For the two-variable minimal model, we find that activation can yield chemical toggles similar to those reported for gene repression in E. coli as well as more complex dynamics.
Keywords: Bistability; Chemical self-replication; Genetic regulation.
Figures
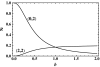


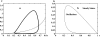
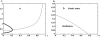
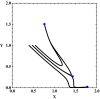

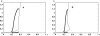
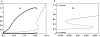
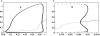

References
-
- Latchman DS. Gene Regulation. 5. New York: Taylor and Francis; 2005.
-
- Ptashne M. A Genetic Switch. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 2004.
-
- Ptashne M, Gann A. Genes and Signals. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 2002.
-
- Alon U. An Introduction to Systems Biology. Boca Raton: Chapman and Hall; 2007.
-
- Aguda BD, Friedman A. Models of Cellular Regulation. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2008.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

