Autoimmunity, end organ damage, and the origin of autoantibodies and autoreactive T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 23449110
- PMCID: PMC3725807
Autoimmunity, end organ damage, and the origin of autoantibodies and autoreactive T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
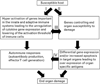
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a prototype of systemic autoimmunity affecting many systems. Both antibodies and autoreactive T cells play significant roles in its pathogenesis. Experimental data and clinical observations indicate that autoimmunity and end organ damage are under separate genetic controls and that there are significant interactions between these two pathways. Experimental evidence has been obtained to support the hypothesis that autoantibodies and autoreactive T effector cells may be initiated by environmental factors through molecular mimicry and the inherent polyreactive nature of antigen receptors. A unified hypothesis has been postulated for the pathogenesis of SLE that has practical implications.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors do not have any known or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus revisited 2011: end organ resistance to damage, autoantibody initiation and diversification, and HLA-DR.J Autoimmun. 2011 Sep;37(2):104-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2011.05.004. Epub 2011 Jun 1. J Autoimmun. 2011. PMID: 21632208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights from murine lupus: disassociation of autoimmunity and end organ damage and the role of T cells.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2005 Sep;17(5):523-8. doi: 10.1097/01.bor.0000169361.23325.1e. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2005. PMID: 16093828 Review.
-
HLA-DR3 restricted T cell epitope mimicry in induction of autoimmune response to lupus-associated antigen SmD.J Autoimmun. 2011 Nov;37(3):254-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2011.07.002. Epub 2011 Aug 24. J Autoimmun. 2011. PMID: 21868195 Free PMC article.
-
B cells biology in systemic lupus erythematosus-from bench to bedside.Sci China Life Sci. 2015 Nov;58(11):1111-25. doi: 10.1007/s11427-015-4953-x. Epub 2015 Nov 13. Sci China Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26563177 Review.
-
Can killers be saviors?Lupus. 2017 Aug;26(9):903-908. doi: 10.1177/0961203316688783. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Lupus. 2017. PMID: 28121242 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbial dysbiosis in the gut drives systemic autoimmune diseases.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 20;13:906258. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.906258. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36341463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-2 protects lupus-prone mice from multiple end-organ damage by limiting CD4-CD8- IL-17-producing T cells.J Immunol. 2014 Sep 1;193(5):2168-77. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400977. Epub 2014 Jul 25. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25063876 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus: immune responses and end organ resistance to damage.Curr Opin Immunol. 2014 Dec;31:87-96. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2014.10.004. Epub 2014 Oct 25. Curr Opin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25458999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet Activation and Thrombus Formation over IgG Immune Complexes Requires Integrin αIIbβ3 and Lyn Kinase.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 20;10(8):e0135738. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135738. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26291522 Free PMC article.
-
B cells regulate thymic CD8+T cell differentiation in lupus-prone mice.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 5;8(52):89486-89499. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19002. eCollection 2017 Oct 27. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29163765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Mayouf SM, Sunker A, Abdwani R, Abrawi SA, Almurshedi F, Alhashmi N, Sonbul A, Sewairi W, Qari A, Abdallah E, Al-Owain M, Al Motywee S, Al-Rayes H, Hashem M, Khalak H, Al-Jebali L, Alkuraya FS. Loss-of-function variant in DNASE1L3 causes a familial form of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet. 2011;43:1186–1188. - PubMed
-
- Bonaci-Nikolic B, Andrejevic S, Pavlovic M, Dimcic Z, Ivanovic B, Nikolic M. Prolonged infections associated with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies specific to proteinase 3 and myeloperoxidase: diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Clin Rheumatol. 2010;29:893–904. - PubMed
-
- Crow MK. Etiology and Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. In: Firestein GS, Budd RC, Gabriel SE, McInnes IB, O'Dell JR, editors. Kelly's Textbook of Rheumatology. Philadelphia PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2013. pp. 1269–1282.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

