A first-in-class, first-in-human, phase I trial of p28, a non-HDM2-mediated peptide inhibitor of p53 ubiquitination in patients with advanced solid tumours
- PMID: 23449360
- PMCID: PMC3619084
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2013.74
A first-in-class, first-in-human, phase I trial of p28, a non-HDM2-mediated peptide inhibitor of p53 ubiquitination in patients with advanced solid tumours
Abstract
Background: This first-in-human, phase I clinical trial of p28 (NSC745104), a 28-amino-acid fragment of the cupredoxin azurin, investigated the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and preliminary activity of p28 in patients with p53(+) metastatic solid tumours.
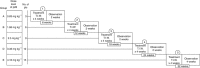
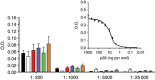
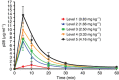
Methods: A total of 15 patients were administered p28 i.v. as a short infusion three times per week for 4 weeks followed by a 2-week rest under an accelerated titration 3+3 dose escalation design until either a grade 3-related adverse event occurred or the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) was reached. Single-dose and steady-state serum pharmacokinetics were characterised. Assessments included toxicity, best objective response by RECIST 1.1 Criteria, and overall survival.
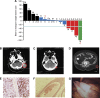
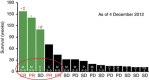
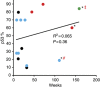
Results: No patients exhibited any dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs), significant adverse events or exhibited an immune response (IgG) to the peptide. The No Observed Adverse Effect Level (NOAEL) and MTD were not reached. Seven patients demonstrated stable disease for 7-61 weeks, three a partial response for 44-125 weeks, and one a complete response for 139 weeks. Three patients are still alive at 158, 140, and 110 weeks post therapy completion.
Conclusion: p28 was tolerated with no significant adverse events. An MTD was not reached. Evidence of anti-tumour activity indicates a highly favourable therapeutic index and demonstrates proof of concept for this new class of non-HDM2-mediated peptide inhibitors of p53 ubiquitination.
Figures
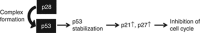
Comment in
-
Targeted therapies: One step closer to drugging p53.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013 May;10(5):246. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2013.43. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23507742 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Preclinical pharmacokinetics, metabolism, and toxicity of azurin-p28 (NSC745104) a peptide inhibitor of p53 ubiquitination.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;68(2):513-24. doi: 10.1007/s00280-010-1518-3. Epub 2010 Nov 18. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21085965
-
Phase I trial of p28 (NSC745104), a non-HDM2-mediated peptide inhibitor of p53 ubiquitination in pediatric patients with recurrent or progressive central nervous system tumors: A Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium Study.Neuro Oncol. 2016 Sep;18(9):1319-25. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/now047. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Neuro Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27022131 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I study of SAR405838, a novel human double minute 2 (HDM2) antagonist, in patients with solid tumours.Eur J Cancer. 2017 May;76:144-151. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2017.02.005. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Eur J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28324749 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase 1, open-label, dose escalation, safety, and pharmacokinetics study of ME-344 as a single agent in patients with refractory solid tumors.Cancer. 2015 Apr 1;121(7):1056-63. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29155. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25411085 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Anticancer Actions of Azurin and Its Derived Peptide p28.Protein J. 2020 Apr;39(2):182-189. doi: 10.1007/s10930-020-09891-3. Protein J. 2020. PMID: 32180097 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Proteomic Method Reveals NLS Tagging of T-DM1 Contravenes Classical Nuclear Transport in a Model of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020 Sep 1;19:99-119. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2020.08.016. eCollection 2020 Dec 11. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020. PMID: 33024794 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the Therapeutic Potential of Biomacromolecules through Intracellular Delivery of Nucleic Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.Adv Healthc Mater. 2022 Jun;11(12):e2102600. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202102600. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022. PMID: 35285167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenovirus-Derived Nano-Capsid Platforms for Targeted Delivery and Penetration of Macromolecules into Resistant and Metastatic Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 19;15(12):3240. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123240. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa derived peptide with iRGD in colon cancer therapy.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023;26(7):768-776. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.68331.14913. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37396945 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide Regulation of Gene Expression: A Systematic Review.Molecules. 2021 Nov 22;26(22):7053. doi: 10.3390/molecules26227053. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34834147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexandroff AB, Jackson AM, O'Donnell MA, James K. BCG immunotherapy of bladder cancer: 20 years on. Lancet. 1999;353 (9165:1689–1694. - PubMed
-
- Anderson KC, Hannah AL, Pazdur R, Farrell AT. A strategic framework for novel drug development in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 2007;138 (2:153–159. - PubMed
-
- Andreeff M, Kojima K, Padmanabhan S, Strair R, Kirschbaum M, Maslak P, Hillmen P, O'Brien S, Samaniego F, Borthakur G, Konopleva M, Vassilev L, Nichols G. A multi-center, open-label, phase i study of single agent RG7112, A first in class p53-MDM2 antagonist, in patients with relapsed/refractory acute myeloid and lymphoid leukemias (AML/ALL) and refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small cell lymphocytic lymphomas (CLL/SCLL) Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2010;116:657.
-
- Arkenau HT, Olmos D, Ang JE, Barriuso J, Karavasilis V, Ashley S, de Bono J, Judson I, Kaye S. 90-Days mortality rate in patients treated within the context of a phase-I trial: how should we identify patients who should not go on trial. Eur J Cancer. 2008;44 (11:1536–1540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

