Actual metal coverage at the neck is critical for flow-diverting stents in treating intracranial aneurysms
- PMID: 23449658
- PMCID: PMC7964893
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A3451
Actual metal coverage at the neck is critical for flow-diverting stents in treating intracranial aneurysms
Figures
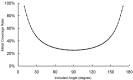
Comment in
-
Reply: To PMID 21852372.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013 Mar;34(3):E33. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.a3514. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013. PMID: 23610782 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
A flow-diverting stent is not a pressure-diverting stent.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013 Jan;34(1):E1-4. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2613. Epub 2011 Aug 18. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013. PMID: 21852372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang K, Huang Q, Hong B, et al. . Correlation of aneurysm occlusion with actual metal coverage at neck after flow-diverting stent implanted in rabbit models. Neuroradiology 2012;54:607–13 - PubMed
-
- Ma D, Dargush GF, Natarajan SK, et al. . Computer modeling of deployment and mechanical expansion of neurovascular flow diverter in patient-specific intracranial aneurysms. J Biomech 2012;45:2256–63 - PubMed
-
- Kulcsár Z, Ernemann U, Wetzel SG, et al. . High-profile flow diverter (Silk) implantation in the basilar artery: efficacy in the treatment of aneurysms and the role of the perforators. Stroke 2010;41:1690–96 - PubMed
-
- Aurboonyawat T, Blanc R, Schmidt P, et al. . An in vitro study of Silk stent morphology. Neuroradiology 2011;53:659–67 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
