Mother-offspring transmission and age-dependent accumulation of simian foamy virus in wild chimpanzees
- PMID: 23449796
- PMCID: PMC3624305
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02743-12
Mother-offspring transmission and age-dependent accumulation of simian foamy virus in wild chimpanzees
Abstract
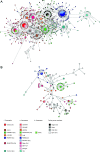
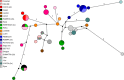
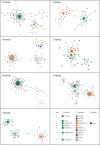
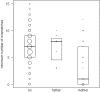
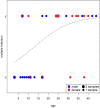
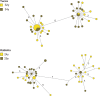
Simian foamy viruses (SFVs) are thought to infect virtually any adult nonhuman primate (NHP). While many data have accumulated about patterns of codivergence with their hosts and cross-species transmission events, little is known about the modalities of SFV transmission within NHP species, especially in the wild. Here we provide a detailed investigation of the dynamics of SFV circulation in a wild community of Western chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus). We demonstrate that mother-offspring (vertical) SFV transmission is common and hypothesize that it accounts for a number of primary infections. We also show that multiple infections with several chimpanzee-specific SFV strains (i.e., superinfection) commonly happen in adult chimpanzees, which might point to adult-specific aggressive behaviors as a lifelong source of SFV infection. Our data give evidence for complex SFV dynamics in wild chimpanzees, even at a single community scale, and show that linking wild NHP social interactions and their microorganisms' dynamics is feasible.
Figures

References
-
- Locatelli S, Peeters M. 2012. Cross-species transmission of simian retroviruses: how and why they could lead to the emergence of new diseases in the human population. AIDS 26:659–673 - PubMed
-
- Liu W, Worobey M, Li Y, Keele BF, Bibollet-Ruche F, Guo Y, Goepfert PA, Santiago ML, Ndjango JB, Neel C, Clifford SL, Sanz C, Kamenya S, Wilson ML, Pusey AE, Gross-Camp N, Boesch C, Smith V, Zamma K, Huffman MA, Mitani JC, Watts DP, Peeters M, Shaw GM, Switzer WM, Sharp PM, Hahn BH. 2008. Molecular ecology and natural history of simian foamy virus infection in wild-living chimpanzees. PLoS Pathog. 4:e1000097 doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000097 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morozov VA, Leendertz FH, Junglen S, Boesch C, Pauli G, Ellerbrok H. 2009. Frequent foamy virus infection in free-living chimpanzees of the Tai National Park (Cote d'Ivoire). J. Gen. Virol. 90:500–506 - PubMed
-
- Switzer WM, Salemi M, Shanmugam V, Gao F, Cong ME, Kuiken C, Bhullar V, Beer BE, Vallet D, Gautier-Hion A, Tooze Z, Villinger F, Holmes EC, Heneine W. 2005. Ancient co-speciation of simian foamy viruses and primates. Nature 434:376–380 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

