A fully attenuated recombinant Salmonid alphavirus becomes pathogenic through a single amino acid change in the E2 glycoprotein
- PMID: 23449806
- PMCID: PMC3648200
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.03501-12
A fully attenuated recombinant Salmonid alphavirus becomes pathogenic through a single amino acid change in the E2 glycoprotein
Abstract
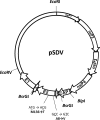
A recombinant sleeping disease virus (rSDV) was previously shown to be totally attenuated and provide long-term protection in trout (C. Moriette, M. Leberre, A. Lamoureux, T. L. Lai, M. Brémont, J. Virol. 80:4088-4098, 2006). Sequence comparison of the rSDV to wild-type genomes exhibited a number of nucleotide changes. In the current study, we demonstrate that the virulent phenotype of SDV was essentially associated with two amino acid changes, V8A and M136T, in the E2 glycoprotein, with the V8A change mostly being involved in the acquisition of the virulent phenotype.
Figures



References
-
- Anonymous 1985. Maladie du sommeil et pollutions expérimentales. Technical report no. 118. Laboratoire National de Pathologie des Animaux Aquatiques, CNEVA, Brest, France
-
- Boucher P, Baudin-Laurencin F. 1994. Sleeping disease of salmonids. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 14:179–180
-
- Boucher P, Castric J, Baudin Laurencin F. 1994. Observation of virus-like particles in rainbow-trout Oncorhynchus mykiss infected with sleeping disease virulent material. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 14:215–216
-
- Castric J, Baudin Laurencin F, Brémont M, Jeffroy J, Le Ven A, Bearzotti M. 1997. Isolation of the virus responsible for sleeping disease in experimentally infected rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 17:27–30
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

