The impact of gene duplication, insertion, deletion, lateral gene transfer and sequencing error on orthology inference: a simulation study
- PMID: 23451112
- PMCID: PMC3581572
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056925
The impact of gene duplication, insertion, deletion, lateral gene transfer and sequencing error on orthology inference: a simulation study
Abstract
The identification of orthologous genes, a prerequisite for numerous analyses in comparative and functional genomics, is commonly performed computationally from protein sequences. Several previous studies have compared the accuracy of orthology inference methods, but simulated data has not typically been considered in cross-method assessment studies. Yet, while dependent on model assumptions, simulation-based benchmarking offers unique advantages: contrary to empirical data, all aspects of simulated data are known with certainty. Furthermore, the flexibility of simulation makes it possible to investigate performance factors in isolation of one another.Here, we use simulated data to dissect the performance of six methods for orthology inference available as standalone software packages (Inparanoid, OMA, OrthoInspector, OrthoMCL, QuartetS, SPIMAP) as well as two generic approaches (bidirectional best hit and reciprocal smallest distance). We investigate the impact of various evolutionary forces (gene duplication, insertion, deletion, and lateral gene transfer) and technological artefacts (ambiguous sequences) on orthology inference. We show that while gene duplication/loss and insertion/deletion are well handled by most methods (albeit for different trade-offs of precision and recall), lateral gene transfer disrupts all methods. As for ambiguous sequences, which might result from poor sequencing, assembly, or genome annotation, we show that they affect alignment score-based orthology methods more strongly than their distance-based counterparts.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



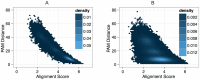
 ; B) with 18 percent ambiguous characters. Scores were normalised by the sum of the aligned characters in both sequences.
; B) with 18 percent ambiguous characters. Scores were normalised by the sum of the aligned characters in both sequences.  .
.

References
-
- Ohno S (1970) Evolution by Gene Duplication. Springer Verlag.
-
- Koonin EV (2005) Orthologs, paralogs, and evolutionary genomics. Annual Review of Genetics 39: 309–338 doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.39.073003.114725. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Altenhoff AM, Studer RA, Robinson-Rechavi M, Dessimoz C (2012) Resolving the ortholog conjecture: orthologs tend to be weakly, but significantly, more similar in function than paralogs. PLoS computational biology 8: e1002514 doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002514. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kristensen DM, Wolf YI, Mushegian AR, Koonin EV (2011) Computational methods for Gene Orthology inference. Briefings in Bioinformatics 12: 379–391 doi:10.1093/bib/bbr030. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Altenhoff AM, Dessimoz C (2012) Inferring orthology and paralogy. In Anisimova M, editor, Evolutionary Genomics, Clifton, NJ: Springer Verlag. pp. 259–279. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-582-4{\-}9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

