Prevalence of sexual, physical and emotional abuse in the Norwegian mother and child cohort study
- PMID: 23452504
- PMCID: PMC3599849
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-186
Prevalence of sexual, physical and emotional abuse in the Norwegian mother and child cohort study
Abstract
Background: Abuse of women occurs in every society of the world. Increased information about the prevalence in industrialized countries, like Norway, is required to make strategies to prevent abuse. Our aim was to investigate the prevalence of self-reported sexual, physical and emotional abuse in a large obstetric population in Norway, and the associations between exposure to adult abuse, socio-demographics and other characteristics.
Methods: Our study is based on the Norwegian Mother and Child (MoBa) Cohort study, conducted by the Norwegian Institute of Public Health. The current study included 65,393 women who responded to two extensive postal questionnaires during pregnancy. Any adult abuse is defined as being exposed to one or more types of adult abuse, any child abuse is defined as being exposed to one or more types of child abuse, and any lifetime abuse is defined as being exposed to abuse either as a child and/or as an adult. Perpetrators were categorized as known or stranger.
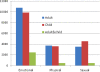
Results: Overall, 32% of the women reported any lifetime abuse, 20% reported any adult abuse, 19% reported any child abuse and 6% reported abuse both as adults and as children. Emotional abuse was the most frequently reported type of abuse both as adults (16%) and children (14%). Adult sexual abuse was reported by 5% and child sexual abuse by 7%. Physical abuse was reported by 6% as adults and by 6% as children. Approximately 30% of those reporting adult or child abuse reported exposure to two or three types of abuse. Five percent of the women reported exposure to any abuse during the last 12 months. For all types of abuse, a known perpetrator was more commonly reported. Logistic regression showed that being exposed to child abuse, smoking and drinking alcohol in the first trimester of pregnancy, living alone, and belonging to the eldest age group were significantly associated with being exposed to any adult abuse.
Conclusion: The reported prevalence of any lifetime abuse was substantial in our low-risk pregnant population. Antenatal care is an opportunity for clinicians to ask about experiences of abuse and identify those at risk.
Figures




References
-
- WHO Department of Gender. Addressing violence against women and achieving the. Millennium Development Goals. 2005.
-
- WHO. Violence against women. 2011. [cited 2012 May]: http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/publications/violence/en/
-
- Bowling A. Research Methods In Health Investigating health and health services. Second edition. Philadelphia: Open University Press Buckingham; 2002.
-
- Jansen HAFM. Interviewer Training in the WHO Multi-Country Study on Women’s Health and Domestic Violence. Violence Against Women. 2004;10:831–849. doi: 10.1177/1077801204265554. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

