Strategies for rapid in vivo 1H and hyperpolarized 13C MR spectroscopic imaging
- PMID: 23453759
- PMCID: PMC3808990
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmr.2013.02.003
Strategies for rapid in vivo 1H and hyperpolarized 13C MR spectroscopic imaging
Abstract
In vivo MRSI is an important imaging modality that has been shown in numerous research studies to give biologically relevant information for assessing the underlying mechanisms of disease and for monitoring response to therapy. The increasing availability of high field scanners and multichannel radiofrequency coils has provided the opportunity to acquire in vivo data with significant improvements in sensitivity and signal to noise ratio. These capabilities may be used to shorten acquisition time and provide increased coverage. The ability to acquire rapid, volumetric MRSI data is critical for examining heterogeneity in metabolic profiles and for relating serial changes in metabolism within the same individual during the course of the disease. In this review we discuss the implementation of strategies that use alternative k-space sampling trajectories and parallel imaging methods in order to speed up data acquisition. The impact of such methods is demonstrated using three recent examples of how these methods have been applied. These are to the acquisition of robust 3D (1)H MRSI data within 5-10 min at a field strength of 3 T, to obtaining higher sensitivity for (1)H MRSI at 7 T and to using ultrafast volumetric and dynamic (13)C MRSI for monitoring the changes in signals that occur following the injection of hyperpolarized (13)C agents.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

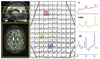


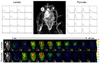
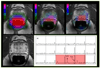
References
-
- Nelson SJ. Analysis of volume MRI and MR spectroscopic imaging data for the evaluation of patients with brain tumors. Magn Reson Med. 2001;46:228–239. - PubMed
-
- Kaiser LG, Young K, Matson GB. Elimination of spatial interference in PRESS-localized editing spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med. 2007 Oct;58(4):813–818. - PubMed
-
- Star-Lack J, Vigneron DB, Pauly J, Kurhanewicz J, Nelson SJ. Improved solvent suppression and increased spatial excitation bandwidths for three-dimensional PRESS CSI using phase-compensating spectral/spatial spin-echo pulses. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1997 Jul-Aug;7(4):745–757. - PubMed
-
- Adalsteinsson E, Irarrazabal P, Topp S, Meyer C, Macovski A, Spielman DM. Volumetric spectroscopic imaging with spiral-based k-space trajectories. Magn Reson Med. 1998 Jun;39(6):889–898. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

