The n-SET domain of Set1 regulates H2B ubiquitylation-dependent H3K4 methylation
- PMID: 23453808
- PMCID: PMC3615140
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.01.034
The n-SET domain of Set1 regulates H2B ubiquitylation-dependent H3K4 methylation
Abstract
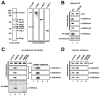
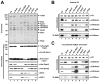
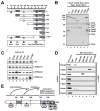
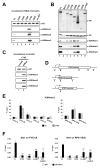
Past studies have documented a crosstalk between H2B ubiquitylation (H2Bub) and H3K4 methylation, but little (if any) direct evidence exists explaining the mechanism underlying H2Bub-dependent H3K4 methylation on chromatin templates. Here, we took advantage of an in vitro histone methyltransferase assay employing a reconstituted yeast Set1 complex (ySet1C) and a recombinant chromatin template containing fully ubiquitylated H2B to gain valuable insights. Combined with genetic analyses, we demonstrate that the n-SET domain within Set1, but not Swd2, is essential for H2Bub-dependent H3K4 methylation. Spp1, a homolog of human CFP1, is conditionally involved in this crosstalk. Our findings extend to the human Set1 complex, underscoring the conserved nature of this disease-relevant crosstalk pathway. As not all members of the H3K4 methyltransferase family contain n-SET domains, our studies draw attention to the n-SET domain as a predictor of an H2B ubiquitylation-sensing mechanism that leads to downstream H3K4 methylation.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Histone Crosstalk: H2Bub and H3K4 Methylation.Mol Cell. 2013 Mar 28;49(6):1019-20. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.03.012. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23541037 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

