Regulated unfolding of proteins in signaling
- PMID: 23454209
- PMCID: PMC4898947
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.02.024
Regulated unfolding of proteins in signaling
Abstract
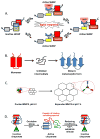
The transduction of biological signals often involves structural rearrangements of proteins in response to input signals, which leads to functional outputs. This review discusses the role of regulated partial and complete protein unfolding as a mechanism of controlling protein function and the prevalence of this regulatory mechanism in signal transduction pathways. The principles of regulated unfolding, the stimuli that trigger unfolding, and the coupling of unfolding with other well characterized regulatory mechanism are discussed.
Copyright © 2013 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Feller G. Protein stability and enzyme activity at extreme biological temperatures. Journal of physics Condensed matter: an Institute of Physics journal. 2010;22:323101. - PubMed
-
- Galea CA, Pagala VR, Obenauer JC, Park CG, Slaughter CA, Kriwacki RW. Proteomic studies of the intrinsically unstructured mammalian proteome. Journal of proteome research. 2006;5:2839–48. - PubMed
-
- Ward JJ, Sodhi JS, McGuffin LJ, Buxton BF, Jones DT. Prediction and functional analysis of native disorder in proteins from the three kingdoms of life. Journal of molecular biology. 2004;337:635–45. - PubMed
-
- Iakoucheva LM, Brown CJ, Lawson JD, Obradovic Z, Dunker AK. Intrinsic disorder in cell-signaling and cancer-associated proteins. Journal of molecular biology. 2002;323:573–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

