BM mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes facilitate multiple myeloma progression
- PMID: 23454749
- PMCID: PMC3613927
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI66517
BM mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes facilitate multiple myeloma progression
Erratum in
- J Clin Invest. 2013 Aug 1;123(8):3635
Abstract
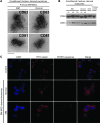
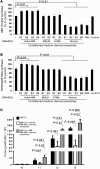
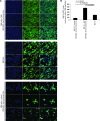
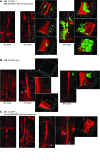
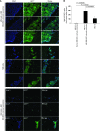
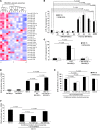
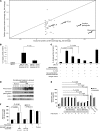
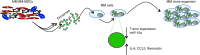
BM mesenchymal stromal cells (BM-MSCs) support multiple myeloma (MM) cell growth, but little is known about the putative mechanisms by which the BM microenvironment plays an oncogenic role in this disease. Cell-cell communication is mediated by exosomes. In this study, we showed that MM BM-MSCs release exosomes that are transferred to MM cells, thereby resulting in modulation of tumor growth in vivo. Exosomal microRNA (miR) content differed between MM and normal BM-MSCs, with a lower content of the tumor suppressor miR-15a. In addition, MM BM-MSC-derived exosomes had higher levels of oncogenic proteins, cytokines, and adhesion molecules compared with exosomes from the cells of origin. Importantly, whereas MM BM-MSC-derived exosomes promoted MM tumor growth, normal BM-MSC exosomes inhibited the growth of MM cells. In summary, these in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that exosome transfer from BM-MSCs to clonal plasma cells represents a previously undescribed and unique mechanism that highlights the contribution of BM-MSCs to MM disease progression.
Figures
References
-
- Chauhan D, et al. Multiple myeloma cell adhesion-induced interleukin-6 expression in bone marrow stromal cells involves activation of NF-kappa B. Blood. 1996;87(3):1104–1112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

