SOCS3 binds specific receptor-JAK complexes to control cytokine signaling by direct kinase inhibition
- PMID: 23454976
- PMCID: PMC3618588
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2519
SOCS3 binds specific receptor-JAK complexes to control cytokine signaling by direct kinase inhibition
Abstract
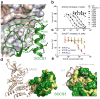
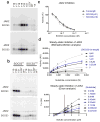
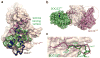
The inhibitory protein SOCS3 plays a key part in the immune and hematopoietic systems by regulating signaling induced by specific cytokines. SOCS3 functions by inhibiting the catalytic activity of Janus kinases (JAKs) that initiate signaling within the cell. We determined the crystal structure of a ternary complex between mouse SOCS3, JAK2 (kinase domain) and a fragment of the interleukin-6 receptor β-chain. The structure shows that SOCS3 binds JAK2 and receptor simultaneously, using two opposing surfaces. While the phosphotyrosine-binding groove on the SOCS3 SH2 domain is occupied by receptor, JAK2 binds in a phosphoindependent manner to a noncanonical surface. The kinase-inhibitory region of SOCS3 occludes the substrate-binding groove on JAK2, and biochemical studies show that it blocks substrate association. These studies reveal that SOCS3 targets specific JAK-cytokine receptor pairs and explains the mechanism and specificity of SOCS action.
Figures




References
-
- Wilks AF, Oates AC. The JAK/STAT pathway. Cancer Surv. 1996;27:139–63. - PubMed
-
- Shuai K, et al. Polypeptide signalling to the nucleus through tyrosine phosphorylation of Jak and Stat proteins. Nature. 1993;366:580–3. - PubMed
-
- Darnell JE, Jr, Kerr IM, Stark GR. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994;264:1415–21. - PubMed
-
- Endo TA, et al. A new protein containing an SH2 domain that inhibits JAK kinases. Nature. 1997;387:921–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

