Lineage-specific functions of Bcl-6 in immunity and inflammation are mediated by distinct biochemical mechanisms
- PMID: 23455674
- PMCID: PMC3604075
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2543
Lineage-specific functions of Bcl-6 in immunity and inflammation are mediated by distinct biochemical mechanisms
Abstract
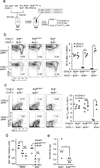
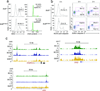
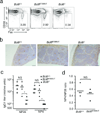
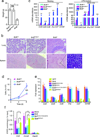
The transcription factor Bcl-6 orchestrates germinal center (GC) reactions through its actions in B cells and T cells and regulates inflammatory signaling in macrophages. Here we found that genetic replacement with mutated Bcl6 encoding Bcl-6 that cannot bind corepressors to its BTB domain resulted in disruption of the formation of GCs and affinity maturation of immunoglobulins due to a defect in the proliferation and survival of B cells. In contrast, loss of function of the BTB domain had no effect on the differentiation and function of follicular helper T cells or that of other helper T cell subsets. Bcl6-null mice had a lethal inflammatory phenotype, whereas mice with a mutant BTB domain had normal healthy lives with no inflammation. The repression of inflammatory responses by Bcl-6 in macrophages was accordingly independent of the repressor function of the BTB domain. Bcl-6 thus mediates its actions through lineage-specific biochemical functions.
Figures



References
-
- Ye BH, et al. Alterations of a zinc finger-encoding gene, BCL-6, in diffuse large-cell lymphoma. Science. 1993;262:747–750. - PubMed
-
- Cattoretti G, et al. BCL-6 protein is expressed in germinal-center B cells. Blood. 1995;86:45–53. - PubMed
-
- Dent AL, Shaffer AL, Yu X, Allman D, Staudt LM. Control of inflammation, cytokine expression, and germinal center formation by BCL-6. Science. 1997;276:589–592. - PubMed
-
- Ye BH, et al. The BCL-6 proto-oncogene controls germinal-centre formation and Th2-type inflammation. Nat Genet. 1997;16:161–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

