Nuclear receptors and their selective pharmacologic modulators
- PMID: 23457206
- PMCID: PMC11060414
- DOI: 10.1124/pr.112.006833
Nuclear receptors and their selective pharmacologic modulators
Abstract
Nuclear receptors are ligand-activated transcription factors and include the receptors for steroid hormones, lipophilic vitamins, sterols, and bile acids. These receptors serve as targets for development of myriad drugs that target a range of disorders. Classically defined ligands that bind to the ligand-binding domain of nuclear receptors, whether they are endogenous or synthetic, either activate receptor activity (agonists) or block activation (antagonists) and due to the ability to alter activity of the receptors are often termed receptor "modulators." The complex pharmacology of nuclear receptors has provided a class of ligands distinct from these simple modulators where ligands display agonist/partial agonist/antagonist function in a tissue or gene selective manner. This class of ligands is defined as selective modulators. Here, we review the development and pharmacology of a range of selective nuclear receptor modulators.
Figures


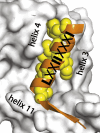
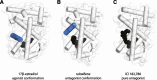



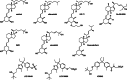
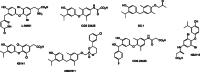




References
-
- Acton JJ, 3rd, Akiyama TE, Chang CH, Colwell L, Debenham S, Doebber T, Einstein M, Liu K, McCann ME, Moller DE, et al. (2009) Discovery of (2R)-2-(3-3-[(4-methoxyphenyl)carbonyl]-2-methyl-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1H-indol-1-ylphenoxy)butanoic acid (MK-0533): a novel selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma modulator for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with a reduced potential to increase plasma and extracellular fluid volume. J Med Chem 52:3846–3854. - PubMed
-
- Acton JJ, 3rd, Black RM, Jones AB, Moller DE, Colwell L, Doebber TW, Macnaul KL, Berger J, Wood HB. (2005) Benzoyl 2-methyl indoles as selective PPARγ modulators. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:357–362. - PubMed
-
- Adams M, Reginato MJ, Shao DL, Lazar MA, Chatterjee VK. (1997) Transcriptional activation by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is inhibited by phosphorylation at a consensus mitogen-activated protein kinase site. J Biol Chem 272:5128–5132. - PubMed
-
- Adorini L. (2002) 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 analogs as potential therapies in transplantation. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 3:1458–1463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

