The insulin receptor: both a prototypical and atypical receptor tyrosine kinase
- PMID: 23457259
- PMCID: PMC3578362
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008946
The insulin receptor: both a prototypical and atypical receptor tyrosine kinase
Abstract
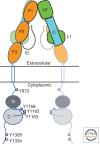
Unlike prototypical receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), which are single-chain polypeptides, the insulin receptor (InsR) is a preformed, covalently linked tetramer with two extracellular α subunits and two membrane-spanning, tyrosine kinase-containing β subunits. A single molecule of insulin binds asymmetrically to the ectodomain, triggering a conformational change that is transmitted to the cytoplasmic kinase domains, which facilitates their trans-phosphorylation. As in prototypical RTKs, tyrosine phosphorylation in the juxtamembrane region of InsR creates recruitment sites for downstream signaling proteins (IRS [InsR substrate] proteins, Shc) containing a phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain, and tyrosine phosphorylation in the kinase activation loop stimulates InsR's catalytic activity. For InsR, phosphorylation of the activation loop, which contains three tyrosine residues, also creates docking sites for adaptor proteins (Grb10/14, SH2B2) that possess specialized Src homology-2 (SH2) domains, which are dimeric and engage two phosphotyrosines in the activation loop.
Figures
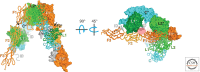
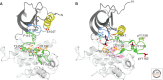
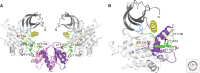
References
-
- Bandyopadhyay D, Kusari A, Kenner KA, Liu F, Chernoff J, Gustafson TA, Kusari J 1997. Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B complexes with the insulin receptor in vivo and is tyrosine-phosphorylated in the presence of insulin. J Biol Chem 272: 1639–1645 - PubMed
-
- Bereziat V, Kasus-Jacobi A, Perdereau D, Cariou B, Girard J, Burnol AF 2002. Inhibition of insulin receptor catalytic activity by the molecular adapter Grb14. J Biol Chem 277: 4845–4852 - PubMed
-
- Bertrand T, Kothe M, Liu J, Dupuy A, Rak A, Berne PF, Davis S, Gladysheva T, Valtre C, Crenne JY, et al. 2012. The crystal structures of TrkA and TrkB suggest key regions for achieving selective inhibition. J Mol Biol 423: 439–453 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
