Probiotics: properties, examples, and specific applications
- PMID: 23457295
- PMCID: PMC3579206
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a010074
Probiotics: properties, examples, and specific applications
Abstract
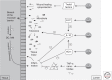
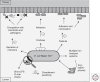
Probiotics are beneficial components of the microbiota that have been used for centuries because of the health benefits they confer to the host. Only recently, however, has the contribution of probiotics to modulation of immunological, respiratory, and gastrointestinal functions started to be fully appreciated and scientifically evaluated. Probiotics such as Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 and lactic acid bacteria are currently used to, or have been evaluated for use to, prevent or treat a range of intestinal maladies including inflammatory bowel disease, constipation, and colon cancer. Engineering these natural probiotics to produce immunomodulatory molecules may help to further increase the benefit to the host. In this article, we will discuss some of the mechanisms of action of probiotics as well as advances in the rational design of probiotics.
Figures

References
-
- Altenhoefer A, Oswald S, Sonnenborn U, Enders C, Schulze J, Hacker J, Oelschlaeger TA 2004. The probiotic Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917 interferes with invasion of human intestinal epithelial cells by different enteroinvasive bacterial pathogens. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 40: 223–229 - PubMed
-
- Andrews NC, Schmidt PJ 2007. Iron homeostasis. Annu Rev Physiol 69: 69–85 - PubMed
-
- Anukam KC, Reid G 2008. Probiotics: 100 years (1907–2007) after Elie Metchnikoff's observations. In Communicating current research and educational topics and trends in applied microbiology, 2007 ed. (ed. Mendez-vilas A), pp. 466–474 Formatex.org, Spain
-
- Artis D 2008. Epithelial-cell recognition of commensal bacteria and maintenance of immune homeostasis in the gut. Nat Rev Immunol 8: 411–420 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
