A multicentre, randomized clinical trial comparing the Veriset™ haemostatic patch with fibrin sealant for the management of bleeding during hepatic surgery
- PMID: 23458162
- PMCID: PMC3692026
- DOI: 10.1111/hpb.12009
A multicentre, randomized clinical trial comparing the Veriset™ haemostatic patch with fibrin sealant for the management of bleeding during hepatic surgery
Abstract
Background: Bleeding during hepatic surgery is associated with prolonged hospitalization and increased morbidity and mortality. The Veriset™ haemostatic patch is a topical haemostat comprised of an absorbable backing made of oxidized cellulose and self-adhesive hydrogel components. It is designed to achieve haemostasis quickly and adhere to tissues without fixation.
Methods: A prospective, randomized, multicentre, single-blinded study (n = 50) was performed to compare the use of a Veriset™ haemostatic patch with a fibrin sealant patch (TachoSil(®) ) (control) in the management of diffuse bleeding after hepatic surgery. Patients were randomized following the confirmation of diffuse bleeding requiring the use of a topical haemostat. Time to haemostasis was assessed at preset intervals until haemostasis was achieved.
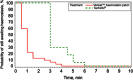
Results: Both groups were similar in comorbidities and procedural techniques. The median time to haemostasis in the group using the Veriset™ haemostatic patch was 1.0 min compared with 3.0 min in the control group (P < 0.001; 3-min minimum application time for the control patch). This result was independent of bleeding severity and surface area. Both products had similar safety profiles and no statistical differences were observed in the occurrence of adverse or device-related events.
Conclusions: Regardless of bleeding severity or surface area, the Veriset™ haemostatic patch achieved haemostasis in this setting significantly faster than the control device in patients undergoing hepatic resection. It was safe and easy to handle in open hepatic surgery.
© 2012 International Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A multicentre, prospective, randomized, controlled trial comparing EVARREST™ fibrin sealant patch to standard of care in controlling bleeding following elective hepatectomy: anatomic versus non-anatomic resection.HPB (Oxford). 2016 Mar;18(3):221-8. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2015.12.006. Epub 2016 Feb 1. HPB (Oxford). 2016. PMID: 27017161 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase III, randomized, controlled, superiority trial evaluating the fibrin pad versus standard of care in controlling parenchymal bleeding during elective hepatic surgery.HPB (Oxford). 2013 Jan;15(1):61-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2012.00583.x. Epub 2012 Oct 16. HPB (Oxford). 2013. PMID: 23216780 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Prospective, Single-Blind, Randomized, Phase III Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Fibrin Sealant Grifols as an Adjunct to Hemostasis During Soft Tissue Open Surgery.J Invest Surg. 2020 Mar;33(3):218-230. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2018.1489917. Epub 2018 Oct 10. J Invest Surg. 2020. PMID: 30303427 Clinical Trial.
-
Fibrin sealant (evicel® [quixil®/crosseal™]): a review of its use as supportive treatment for haemostasis in surgery.Drugs. 2011 Oct 1;71(14):1893-915. doi: 10.2165/11207700-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21942978 Review.
-
Fibrin and Thrombin Sealants in Vascular and Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2020 Sep;60(3):469-478. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2020.05.016. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 32620348
Cited by
-
New polyoxazoline loaded patches for hemostasis in experimental liver resection.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2022 Mar;110(3):597-605. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.34938. Epub 2021 Sep 18. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2022. PMID: 34536065 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and effectiveness of a synthetic hemostatic patch for intraoperative soft tissue bleeding.Med Devices (Auckl). 2015 Mar 31;8:167-74. doi: 10.2147/MDER.S79556. eCollection 2015. Med Devices (Auckl). 2015. PMID: 25878513 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized comparison of an adhesive gelatin sponge and a plain collagen sponge for hemostatic control during canine liver surgery.Vet Surg. 2025 Feb;54(2):345-353. doi: 10.1111/vsu.14160. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Vet Surg. 2025. PMID: 39378152 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized, controlled comparison of advanced hemostatic pads in hepatic surgical models.ISRN Surg. 2014 Mar 4;2014:930803. doi: 10.1155/2014/930803. eCollection 2014. ISRN Surg. 2014. PMID: 24729905 Free PMC article.
-
Versatility and clinical effectiveness of a synthetic sealing hemostatic patch as alternative to parenchyma suturing in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy.Surg Endosc. 2022 Jan;36(1):663-669. doi: 10.1007/s00464-021-08333-0. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Surg Endosc. 2022. PMID: 33591449 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nathan H, Segev DL, Mayo SC, Choti MA, Cameron AM, Wolfgang CL, et al. National trends in surgical procedures for hepatocellular carcinoma: 1998–2008. Cancer. 2012;118:1838–1844. - PubMed
-
- Boucher BA, Traub O. Achieving haemostasis in the surgical field. Pharmacotherapy. 2009;29(Suppl. 7 Pt 2):2–7. - PubMed
-
- Carson JL, Poses RM, Spence RK, Bonavita G. Severity of anaemia and operative mortality and morbidity. Lancet. 1988;1:727–729. - PubMed
-
- de Boer MT, Molenaar IQ, Porte RJ. Impact of blood loss on outcome after liver resection. Dig Surg. 2007;24:259–264. - PubMed
-
- Farid SG, Aldouri A, Morris-Stiff G, Khan AZ, Toogood GJ, Lodge JP, et al. Correlation between postoperative infective complications and longterm outcomes after hepatic resection for colorectal liver metastasis. Ann Surg. 2010;251:91–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

