Aplysqualenols A and B: Squalene-Derived Polyethers with Antitumoral and Antiviral Activity from the Caribbean Sea Slug Aplysia dactylomela
- PMID: 23459021
- PMCID: PMC3583239
- DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.200900775
Aplysqualenols A and B: Squalene-Derived Polyethers with Antitumoral and Antiviral Activity from the Caribbean Sea Slug Aplysia dactylomela
Abstract
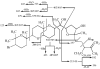
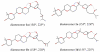
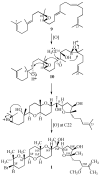
The novel bromotriterpene polyethers aplysqualenol A (1) and aplysqualenol B (2) have been isolated from the Caribbean sea slug Aplysia dactylomela collected in Puerto Rico, and their structures and relative configurational assignments established from spectroscopic data aided by quantum mechanical calculations of NMR chemical shifts. Although both these compounds may be conceived as polyoxycyclic derivatives of the C30 squalene skeleton, remarkably 1 and 2 possess an unprecedented C15 to C24 flexible chain of 14S* spatial disposition that contains a unique ether bridge between C16 and C19. Biological activity screening tests revealed that, although aplysqualenol A (1) does not have significant anti-infective properties, it possesses potent antitumoral and antiviral activities.
Keywords: Antitumor activity; Antiviral activity; Aplysia dactylomela; Polyether; Sea slug.
Figures

References
-
- Blunt JW, Copp BR, Hu W-P, Munro MHG, Northcote PT, Prinsep MR. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009;26:170–244. and previous articles in this series. - PubMed
-
- Ferrigni NR, Meyer BN, Putnam JE, Jacobsen LB, Nichols DE, McLaughlin JL. J. Med. Plant Res. 1982;45:31–34. - PubMed
-
- Fernández JJ, Souto ML, Norte M. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2000;17:235–246. - PubMed
-
- Blunt JW, Hartshorn MP, McLennan TJ, Munro MHG, Robinson WT, Yorke SC. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978:69–72.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
