Regulation of molecular chaperones through post-translational modifications: decrypting the chaperone code
- PMID: 23459247
- PMCID: PMC4492711
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.02.010
Regulation of molecular chaperones through post-translational modifications: decrypting the chaperone code
Abstract
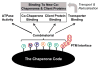
Molecular chaperones and their associated cofactors form a group of highly specialized proteins that orchestrate the folding and unfolding of other proteins and the assembly and disassembly of protein complexes. Chaperones are found in all cell types and organisms, and their activity must be tightly regulated to maintain normal cell function. Indeed, deregulation of protein folding and protein complex assembly is the cause of various human diseases. Here, we present the results of an extensive review of the literature revealing that the post-translational modification (PTM) of chaperones has been selected during evolution as an efficient mean to regulate the activity and specificity of these key proteins. Because the addition and reciprocal removal of chemical groups can be triggered very rapidly, this mechanism provides an efficient switch to precisely regulate the activity of chaperones on specific substrates. The large number of PTMs detected in chaperones suggests that a combinatory code is at play to regulate function, activity, localization, and substrate specificity for this group of biologically important proteins. This review surveys the core information currently available as a starting point toward the more ambitious endeavor of deciphering the "chaperone code".
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


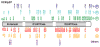
Similar articles
-
Post-translational modifications of Hsp70 family proteins: Expanding the chaperone code.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 31;295(31):10689-10708. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.011666. Epub 2020 Jun 9. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32518165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms targeting apolipoprotein B100 to proteasomal degradation: evidence that degradation is initiated by BiP binding at the N terminus and the formation of a p97 complex at the C terminus.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009 Apr;29(4):579-85. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.181859. Epub 2009 Jan 22. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009. PMID: 19164805
-
Mitochondrial Chaperone Code: Just warming up.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2024 Jun;29(3):483-496. doi: 10.1016/j.cstres.2024.05.002. Epub 2024 May 17. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2024. PMID: 38763405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cdc37-Hsp90 complexes are responsive to nucleotide-induced conformational changes and binding of further cofactors.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 24;285(52):40921-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.131086. Epub 2010 Sep 29. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20880838 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular chaperones HscA/Ssq1 and HscB/Jac1 and their roles in iron-sulfur protein maturation.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 Mar-Apr;42(2):95-111. doi: 10.1080/10409230701322298. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17453917 Review.
Cited by
-
Virus-pathogen interactions improve water quality along the Middle Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Canal.ISME J. 2023 Oct;17(10):1719-1732. doi: 10.1038/s41396-023-01481-2. Epub 2023 Jul 31. ISME J. 2023. PMID: 37524909 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular chaperone TRiC/CCT binds to the Trp-Asp 40 (WD40) repeat protein WDR68 and promotes its folding, protein kinase DYRK1A binding, and nuclear accumulation.J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 28;289(48):33320-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.586115. Epub 2014 Oct 22. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25342745 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive characterization of the Hsp70 interactome reveals novel client proteins and interactions mediated by posttranslational modifications.PLoS Biol. 2022 Oct 21;20(10):e3001839. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001839. eCollection 2022 Oct. PLoS Biol. 2022. PMID: 36269765 Free PMC article.
-
Growth-Regulated Hsp70 Phosphorylation Regulates Stress Responses and Prion Maintenance.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 May 28;40(12):e00628-19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00628-19. Print 2020 May 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32205407 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological Outcomes Mediated Upon Binding of Heat Shock Proteins to Scavenger Receptors SCARF1 and LOX-1, and Endocytosis by Mononuclear Phagocytes.Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 10;10:3035. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03035. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31998315 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tissieres A, Mitchell HK, Tracy UM. Protein synthesis in salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: relation to chromosome puffs. J Mol Biol. 1974;84:389–398. - PubMed
-
- Frydman J, Nimmesgern E, Ohtsuka K, Hartl FU. Folding of nascent polypeptide chains in a high molecular mass assembly with molecular chaperones. Nature. 1994;370:111–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

