Adolescent-onset alcohol abuse exacerbates the influence of childhood conduct disorder on late adolescent and early adult antisocial behaviour
- PMID: 23459369
- PMCID: PMC3583014
- DOI: 10.1080/14789949.2011.641996
Adolescent-onset alcohol abuse exacerbates the influence of childhood conduct disorder on late adolescent and early adult antisocial behaviour
Abstract
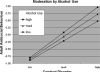
This study tested the hypothesis that adolescent-onset alcohol abuse (AOAA) would both mediate and moderate the effect of childhood conduct disorder on antisocial behaviour in late adolescence and early adulthood. A sample comprising 504 young men and women strategically recruited from the community were grouped using the criteria of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-IV, American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: APA), as follows: neither childhood conduct disorder (CCD) nor alcohol abuse/dependence; CCD but no alcohol abuse or dependence; alcohol abuse/dependence but no CCD; both CCD and alcohol abuse/dependence. The outcome measure was the sum of positive responses to 55 interview items capturing a variety of antisocial behaviours engaged in since age 15. Severity of lifetime alcohol-related and CCD problems served as predictor variables in regression analysis. Antisocial behaviour problems were greatest in individuals with a history of co-occurring conduct disorder (CD) and alcohol abuse/dependence. While CCD was strongly predictive of adult antisocial behaviour, this effect was both mediated and moderated (exacerbated) by AOAA.
Keywords: alcohol abuse; antisocial behaviour; conduct disorder.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship between childhood conduct disorder and adult antisocial behavior is partially mediated by early-onset alcohol abuse.Personal Disord. 2012 Oct;3(4):423-32. doi: 10.1037/a0027017. Epub 2012 Aug 13. Personal Disord. 2012. PMID: 22888992
-
Re-offending in forensic patients released from secure care: the role of antisocial/borderline personality disorder co-morbidity, substance dependence and severe childhood conduct disorder.Crim Behav Ment Health. 2013 Jul;23(3):191-202. doi: 10.1002/cbm.1852. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Crim Behav Ment Health. 2013. PMID: 23371302
-
Antisocial personality disorder with childhood- vs. adolescence-onset conduct disorder: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions.J Nerv Ment Dis. 2006 Sep;194(9):667-75. doi: 10.1097/01.nmd.0000235762.82264.a1. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2006. PMID: 16971818
-
Prevalence, correlates, and comorbidity of DSM-IV antisocial personality syndromes and alcohol and specific drug use disorders in the United States: results from the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions.J Clin Psychiatry. 2005 Jun;66(6):677-85. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v66n0602. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 15960559
-
[Evaluation of typical psychopathic traits with juvenile offenders].Encephale. 2004 Jul-Aug;30(4):369-75. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(04)95450-4. Encephale. 2004. PMID: 15597464 French.
Cited by
-
High School Sports Involvement Diminishes the Association Between Childhood Conduct Disorder and Adult Antisocial Behavior.J Adolesc Health. 2015 Jul;57(1):107-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2015.03.009. Epub 2015 Apr 28. J Adolesc Health. 2015. PMID: 25937472 Free PMC article.
-
Personality disorders and violence: what is the link?Borderline Personal Disord Emot Dysregul. 2015 Sep 17;2:12. doi: 10.1186/s40479-015-0033-x. eCollection 2015. Borderline Personal Disord Emot Dysregul. 2015. PMID: 26401314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dare to delay? The impacts of adolescent alcohol and marijuana use onset on cognition, brain structure, and function.Front Psychiatry. 2013 Jul 1;4:53. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00053. eCollection 2013. Front Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23847550 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol Use and Moffitt's Maturity Gap Thesis for Adolescent Offending: An Evolutionary Perspective and Analysis.Evol Psychol. 2024 Jan-Mar;22(1):14747049241241432. doi: 10.1177/14747049241241432. Evol Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38528754 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative and complementary reinforcers as mechanisms linking adolescent conduct problems and substance use.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2016 Oct;24(5):376-389. doi: 10.1037/pha0000088. Epub 2016 Aug 15. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27690501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aiken LS, West SG. Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Sage; Newbury Park, CA: 1991.
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th ed. APA; Washington, DC: 1994.
-
- Bakken K, Landheim AS, Vaglum P. Early and late onset groups of substance misusers: Differences in primary and secondary psychiatric disorders. Journal of Substance Use. 2004;9:224–234.
-
- Bauer LO, Hesselbrock VM. EEG, autonomic and subjective correlates of the risk for alcoholism. Journal of Studies on Alcohol. 1993;54:577–589. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein DP, Cohen P, Skodol A, Bezirganian S, Brook JS. Childhood antecedents of adolescent personality disorders. American Journal of Psychiatry. 1996;153:907–913. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
