Randomized dose-ranging study of the 14-day early bactericidal activity of bedaquiline (TMC207) in patients with sputum microscopy smear-positive pulmonary tuberculosis
- PMID: 23459487
- PMCID: PMC3632959
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02243-12
Randomized dose-ranging study of the 14-day early bactericidal activity of bedaquiline (TMC207) in patients with sputum microscopy smear-positive pulmonary tuberculosis
Abstract
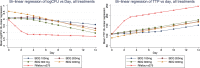
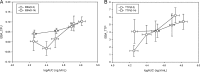
Bedaquiline is a new antituberculosis agent targeting ATP synthase. This randomized, double-blinded study enrolling 68 sputum smear-positive pulmonary tuberculosis patients evaluated the 14-day early bactericidal activity of daily doses of 100 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg bedaquiline, preceded by loading doses of 200 mg, 400 mg, 500 mg, and 700 mg, respectively, on the first treatment day and 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg, and 500 mg on the second treatment day. All groups showed activity with a mean (standard deviation) daily fall in log10 CFU over 14 days of 0.040 (0.068), 0.056 (0.051), 0.077 (0.064), and 0.104 (0.077) in the 100-mg, 200-mg, 300-mg, and 400-mg groups, respectively. The linear trend for dose was significant (P = 0.001), and activity in the 400-mg dose group was greater than that in the 100-mg group (P = 0.014). All of the bedaquiline groups showed significant bactericidal activity that was continued to the end of the 14-day evaluation period. The finding of a linear trend for dose suggests that the highest dose compatible with safety considerations should be taken forward to longer-term clinical studies.
Figures

Comment in
-
Dose-ranging activity of the newly registered antituberculosis drug bedaquiline (TMC207).Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2013 Jul;11(7):649-51. doi: 10.1586/14787210.2013.811848. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2013. PMID: 23879605
References
-
- Andries K, Verhasselt P, Guillemont J, Gohlmann HW, Neefs JM, Winkler H, Van Gestel J, Timmerman P, Zhu M, Lee E, Williams P, de Chaffoy D, Huitric E, Hoffner S, Cambau E, Truffot-Pernot C, Lounis N, Jarlier V. 2005. A diarylquinoline drug active on the ATP synthase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science 307:223–227 - PubMed
-
- Rustomjee R, Diacon AH, Allen J, Venter A, Reddy C, Patientia RF, Mthiyane TC, De Marez T, van Heeswijk R, Kerstens R, Koul A, De Beule K, Donald PR, McNeeley DF. 2008. Early bactericidal activity and pharmacokinetics of the diarylquinoline TMC207 in treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52:2831–2835 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Diacon AH, Pym A, Grobusch M, Patientia R, Rustomjee R, Page-Shipp L, Pistorius C, Krause R, Bogoshi M, Churchyard G, Venter A, Allen J, Palomino JC, De Marez T, van Heeswijk RP, Lounis N, Meyvisch P, Verbeeck J, Parys W, de Beule K, Andries K, McNeeley DF. 2009. The diarylquinoline TMC207 for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 360:2397–2405 - PubMed
-
- Diacon AH, Donald PR, Pym A, Grobusch M, Patientia RF, Mahanyele R, Bantubani N, Narasimooloo R, De Marez T, van Heeswijk R, Lounis N, Meyvisch P, Andries K, McNeeley DF. 2012. Randomized pilot trial of eight weeks of bedaquiline (TMC207) treatment for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: long-term outcome, tolerability, and effect on emergence of drug resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 56:3271–3276 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rieder HL, Van Deun A, Kam KM, Kim SJ, Chonde TM, Trébucq A, Urbanczik R. 2007. Priorities for tuberculosis bacteriology services in low-income countries, 2nd ed International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease (The Union), Paris, France
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

