The role of estrogens in control of energy balance and glucose homeostasis
- PMID: 23460719
- PMCID: PMC3660717
- DOI: 10.1210/er.2012-1055
The role of estrogens in control of energy balance and glucose homeostasis
Abstract
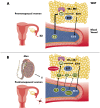
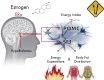
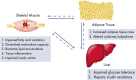
Estrogens play a fundamental role in the physiology of the reproductive, cardiovascular, skeletal, and central nervous systems. In this report, we review the literature in both rodents and humans on the role of estrogens and their receptors in the control of energy homeostasis and glucose metabolism in health and metabolic diseases. Estrogen actions in hypothalamic nuclei differentially control food intake, energy expenditure, and white adipose tissue distribution. Estrogen actions in skeletal muscle, liver, adipose tissue, and immune cells are involved in insulin sensitivity as well as prevention of lipid accumulation and inflammation. Estrogen actions in pancreatic islet β-cells also regulate insulin secretion, nutrient homeostasis, and survival. Estrogen deficiency promotes metabolic dysfunction predisposing to obesity, the metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes. We also discuss the effect of selective estrogen receptor modulators on metabolic disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Keating NL, Cleary PD, Rossi AS, Zaslavsky AM, Ayanian JZ. Use of hormone replacement therapy by postmenopausal women in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130:545–553. - PubMed
-
- Ziel HK, Finkle WD. Increased risk of endometrial carcinoma among users of conjugated estrogens. N Engl J Med. 1975;293:1167–1170. - PubMed
-
- Smith DC, Prentice R, Thompson DJ, Herrmann WL. Association of exogenous estrogen and endometrial carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1975;293:1164–1167. - PubMed
-
- Rossouw JE, Anderson GL, Prentice RL, et al. Risks and benefits of estrogen plus progestin in healthy postmenopausal women: principal results from the Women's Health Initiative randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2002;288:321–333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 DK088761/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK074970/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK069362/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK078760/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK074970/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078760/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HD044405/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089109/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK088761/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK069362/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK088220/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK073689/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK088220/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD044405/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK073689/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK089109/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

