IL-1 enhances expansion, effector function, tissue localization, and memory response of antigen-specific CD8 T cells
- PMID: 23460726
- PMCID: PMC3600912
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20122006
IL-1 enhances expansion, effector function, tissue localization, and memory response of antigen-specific CD8 T cells
Abstract
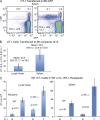
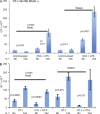
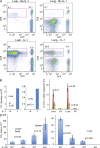
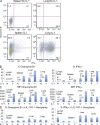
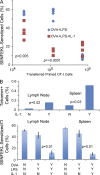
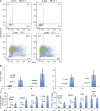
Here, we show that interleukin-1 (IL-1) enhances antigen-driven CD8 T cell responses. When administered to recipients of OT-I T cell receptor transgenic CD8 T cells specific for an ovalbumin (OVA) peptide, IL-1 results in an increase in the numbers of wild-type but not IL1R1(-/-) OT-I cells, particularly in spleen, liver, and lung, upon immunization with OVA and lipopolysaccharide. IL-1 administration also results in an enhancement in the frequency of antigen-specific cells that are granzyme B(+), have cytotoxic activity, and/ or produce interferon γ (IFN-γ). Cells primed in the presence of IL-1 display enhanced expression of granzyme B and increased capacity to produce IFN-γ when rechallenged 2 mo after priming. In three in vivo models, IL-1 enhances the protective value of weak immunogens. Thus, IL-1 has a marked enhancing effect on antigen-specific CD8 T cell expansion, differentiation, migration to the periphery, and memory.
Figures

References
-
- Curtsinger J.M., Schmidt C.S., Mondino A., Lins D.C., Kedl R.M., Jenkins M.K., Mescher M.F. 1999. Inflammatory cytokines provide a third signal for activation of naive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. J. Immunol. 162:3256–3262 - PubMed
-
- Ding Z., Xiong K., Issekutz T.B. 2000. Regulation of chemokine-induced transendothelial migration of T lymphocytes by endothelial activation: differential effects on naive and memory T cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 67:825–833 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

