Use of pre-operative steroids in liver resection: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 23461716
- PMCID: PMC3892310
- DOI: 10.1111/hpb.12066
Use of pre-operative steroids in liver resection: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: By attenuating the systemic inflammatory response to major surgery, the pre-operative administration of steroids may reduce the incidence of complications.
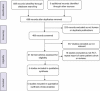
Methods: A systematic review was conducted to identify randomized controlled trials (RCT) comparing pre-operative steroid administration with placebo during a liver resection. Meta-analyses were performed.
Results: Five RCTs were identified including a total of 379 patients. Pre-operative steroids were associated with statistically significant reductions in the levels of serum bilirubin and interleukin 6 (IL-6) on post-operative day one. There was a trend towards a lower incidence of post-operative complications and prothrombin time (PT), but this did not reach statistical significance.
Conclusion: Pre-operative steroids may be associated with a clinically significant benefit in liver resection.
© 2013 International Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Association.
Figures


References
-
- Faist E, Schinkel C, Zimmer S. Update on the mechanisms of immune suppression of injury and immune modulation. World J Surg. 1996;20:454–459. - PubMed
-
- Hill AG. Initiators and propagators of the metabolic response to injury. World J Surg. 2000;24:624–629. - PubMed
-
- Robertson CM, Coopersmith CM. The systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Microbes Infect. 2006;8:1382–1389. - PubMed
-
- Kehlet H, Dahl JB. Anaesthesia, surgery, and challenges in postoperative recovery. Lancet. 2003;362:1921–1928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

