Human hypocretin and melanin-concentrating hormone levels are linked to emotion and social interaction
- PMID: 23462990
- PMCID: PMC3595130
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms2461
Human hypocretin and melanin-concentrating hormone levels are linked to emotion and social interaction
Abstract
The neurochemical changes underlying human emotions and social behaviour are largely unknown. Here we report on the changes in the levels of two hypothalamic neuropeptides, hypocretin-1 and melanin-concentrating hormone, measured in the human amygdala. We show that hypocretin-1 levels are maximal during positive emotion, social interaction and anger, behaviours that induce cataplexy in human narcoleptics. In contrast, melanin-concentrating hormone levels are minimal during social interaction, but are increased after eating. Both peptides are at minimal levels during periods of postoperative pain despite high levels of arousal. Melanin-concentrating hormone levels increase at sleep onset, consistent with a role in sleep induction, whereas hypocretin-1 levels increase at wake onset, consistent with a role in wake induction. Levels of these two peptides in humans are not simply linked to arousal, but rather to specific emotions and state transitions. Other arousal systems may be similarly emotionally specialized.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
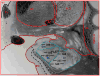
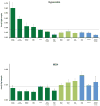
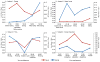
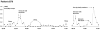
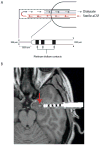
References
-
- Peyron C, et al. A mutation in a case of early onset narcolepsy and a generalized absence of hypocretin peptides in human narcoleptic brains. Nat Med. 2000;6:991–997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- IK6 BX005245/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 DA034748/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- NS14610/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS033310/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS014610/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX001753/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 NS033310/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH064109/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS014610/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS02808/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS33310/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 NS033310/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS002808/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH064109/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

