Neuron-released oligomeric α-synuclein is an endogenous agonist of TLR2 for paracrine activation of microglia
- PMID: 23463005
- PMCID: PMC4089961
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms2534
Neuron-released oligomeric α-synuclein is an endogenous agonist of TLR2 for paracrine activation of microglia
Abstract
Abnormal aggregation of α-synuclein and sustained microglial activation are important contributors to the pathogenic processes of Parkinson's disease. However, the relationship between disease-associated protein aggregation and microglia-mediated neuroinflammation remains unknown. Here, using a combination of in silico, in vitro and in vivo approaches, we show that extracellular α-synuclein released from neuronal cells is an endogenous agonist for Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), which activates inflammatory responses in microglia. The TLR2 ligand activity of α-synuclein is conformation-sensitive; only specific types of oligomer can interact with and activate TLR2. This paracrine interaction between neuron-released oligomeric α-synuclein and TLR2 in microglia suggests that both of these proteins are novel therapeutic targets for modification of neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease and related neurological diseases.
Figures


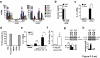


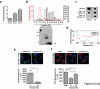
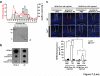
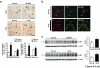
References
-
- Hirsch EC, Hunot S. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease: a target for neuroprotection? Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:382–397. - PubMed
-
- Graeber MB, Streit WJ. Microglia: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010;119:89–105. - PubMed
-
- Kim C, Lee S-J. Controlling the mass action of alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 2008;107:303–316. - PubMed
-
- Jang A, et al. Non-classical exocytosis of alpha-synuclein is sensitive to folding states and promoted under stress conditions. J Neurochem. 2010;113:1263–1274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

