Novel progranulin mutations with reduced serum-progranulin levels in frontotemporal lobar degeneration
- PMID: 23463024
- PMCID: PMC3798842
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2013.37
Novel progranulin mutations with reduced serum-progranulin levels in frontotemporal lobar degeneration
Abstract
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease with an age at onset generally below 65 years. Mutations in progranulin (GRN) have been reported to be able to cause FTLD through haploinsufficiency. We have sequenced GRN in 121 patients with FTLD and detected six different mutations in eight patients: p.Gly35Glufs*19, p.Asn118Phefs*4, p.Val200Glyfs*18, p.Tyr294*, p.Cys404* and p.Cys416Leufs*30. Serum was available for five of the mutations, where the serum-GRN levels were found to be >50% reduced compared with FTLD patients without GRN mutations. Moreover, the p.Cys416Leufs*30 mutation segregated in an affected family with different dementia diagnoses. The mutation frequency of GRN mutation was 6.6% in our FTLD cohort.
Figures

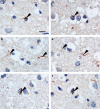
References
-
- McKhann GM, Albert MS, Grossman M, Miller B, Dickson D, Trojanowski JQ. Clinical and pathological diagnosis of frontotemporal dementia: report of the Work Group on Frontotemporal Dementia and Pick's Disease. Arch Neurol. 2001;58:1803–1809. - PubMed
-
- Neary D, Snowden JS, Gustafson L, et al. Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a consensus on clinical diagnostic criteria. Neurology. 1998;51:1546–1554. - PubMed
-
- Lomen-Hoerth C, Anderson T, Miller B. The overlap of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Neurology. 2002;59:1077–1079. - PubMed
-
- Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P, et al. Association of missense and 5′-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature. 1998;393:702–705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

