Functional implications of genome topology
- PMID: 23463314
- PMCID: PMC6320674
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2474
Functional implications of genome topology
Abstract
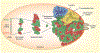
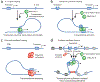
Although genomes are defined by their sequence, the linear arrangement of nucleotides is only their most basic feature. A fundamental property of genomes is their topological organization in three-dimensional space in the intact cell nucleus. The application of imaging methods and genome-wide biochemical approaches, combined with functional data, is revealing the precise nature of genome topology and its regulatory functions in gene expression and genome maintenance. The emerging picture is one of extensive self-enforcing feedback between activity and spatial organization of the genome, suggestive of a self-organizing and self-perpetuating system that uses epigenetic dynamics to regulate genome function in response to regulatory cues and to propagate cell-fate memory.
Figures
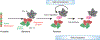
References
-
- Lanctot C, Cheutin T, Cremer M, Cavalli G & Cremer T Dynamic genome architecture in the nuclear space: regulation of gene expression in three dimensions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 8, 104–115 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Misteli T Beyond the sequence: Cellular organization of genome function. Cell 128, 787–800 (2007). - PubMed
-
-
Rajapakse I & Groudine M On emerging nuclear order. J. Cell Biol. 192, 711–721 (2011).
This comprehensive overview of basic principles of genome organization includes a discussion of the concept of self-organized genome architecture.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

