Cohesin at active genes: a unifying theme for cohesin and gene expression from model organisms to humans
- PMID: 23465542
- PMCID: PMC3691354
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2013.02.003
Cohesin at active genes: a unifying theme for cohesin and gene expression from model organisms to humans
Abstract
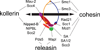
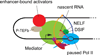
Cohesin is an evolutionarily ancient multisubunit protein complex with a deeply conserved function: it provides cohesion between sister chromatids from the time of DNA replication in S-phase until mitosis. This cohesion facilitates repair of damage that occurs during DNA replication, and, crucially, enforces faithful segregation of chromosomes upon cell division. Cohesin also influences gene expression, and relative to sister chromatid cohesion, gene expression is exquisitely sensitive to moderate changes in cohesin activity. Early studies revealed differences in cohesin's roles in gene expression between various organisms. In all organisms examined, however, cohesin marks a subset of active genes. This review focuses on the roles of cohesin at active genes, and to what extent these roles are conserved between organisms.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Nasmyth K, Haering CH. Cohesin: its roles and mechanisms. Annu Rev Genet. 2009;43:525–558. - PubMed
-
- Krantz ID, McCallum J, DeScipio C, Kaur M, Gillis LA, Yaeger D, Jukofsky L, Wasserman N, Bottani A, Morris CA, Nowaczyk MJ, Toriello H, Bamshad MJ, Carey JC, Rappaport E, Kawauchi S, Lander AD, Calof AL, Li HH, Devoto M, Jackson LG. Cornelia de Lange syndrome is caused by mutations in NIPBL, the human homolog of Drosophila melanogaster Nipped-B. Nat Genet. 2004;36:631–635. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tonkin ET, Wang TJ, Lisgo S, Bamshad MJ, Strachan T. NIPBL, encoding a homolog of fungal Scc2-type sister chromatid cohesion proteins and fly Nipped-B, is mutated in Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Nat Genet. 2004;36:636–641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

