Accumulation of cadmium in insulin-producing β cells
- PMID: 23466887
- PMCID: PMC3605169
- DOI: 10.4161/isl.23101
Accumulation of cadmium in insulin-producing β cells
Abstract
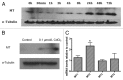
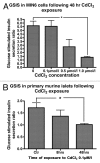
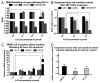
Evidence suggests that chronic low level cadmium exposure impairs the function of insulin-producing β cells and may be associated with type-2 diabetes mellitus. Herein, we describe the cadmium content in primary human islets and define the uptake kinetics and effects of environmentally relevant cadmium concentrations in cultured β cells. The average cadmium content in islets from 10 non-diabetic human subjects was 29 ± 7 nmol/g protein (range 7 to 72 nmol/g protein). Exposure of the β-cell line MIN6 to CdCl 2 concentrations between 0.1 and 1.0 µmol/L resulted in a dose- and time-dependent uptake of cadmium over 72 h. This uptake resulted in an induction of metallthionein expression, likely enhancing cellular cadmium accumulation. Furthermore, cadmium accumulation resulted in an inhibition of glucose stimulated insulin secretion in MIN6 cells and primary mouse islets. Our results indicate that this impairment in β-cell function is not due to an increase in cell death or due to an increase in oxidative stress. We conclude that mouse β cells accumulate cadmium in a dose- and time-dependent manner over a prolonged time course at environmentally relevant concentrations. This uptake leads to a functional impairment of β-cell function without significant alterations in cell viability, expression of genes important for β-cell function or increase in oxidative stress.
Keywords: cadmium; insulin secretion; metallothionein; zinc transporters; β cells.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50HD044405/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA151461/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000150/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM038784/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD057450/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA151461/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HD057450/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37GM038784/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 ES020880/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- 1K08ES020880-01/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD044405/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
