miR-29c is downregulated in renal interstitial fibrosis in humans and rats and restored by HIF-α activation
- PMID: 23467423
- PMCID: PMC3651624
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00287.2012
miR-29c is downregulated in renal interstitial fibrosis in humans and rats and restored by HIF-α activation
Abstract
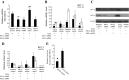
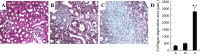
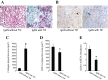
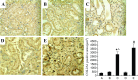
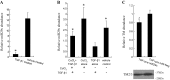
Treatment with L-mimosine, which activates hypoxia-inducible factor-α (HIF-α), attenuates renal tubulointerstitial injury and improves renal function in a rat remnant kidney model. The miR-29 family of microRNAs directly targets a large number of extracellular matrix genes and reduces renal interstitial fibrosis. We analyzed microRNA expression profiles in rat remnant kidneys with or without treatment with L-mimosine. The expression of miR-29c was downregulated in rat remnant kidneys compared with sham control and significantly restored by the L-mimosine treatment. In cultured human kidney epithelial HK2 cells, cobalt chloride activated HIF-α and upregulated miR-29c expression. The upregulation of miR-29c expression was significantly attenuated by knockdown of HIF-1α or HIF-2α. Downregulation of miR-29c was associated with significant increases in interstitial fibrosis, collagen type II α1 (COL2A1) protein, and tropomyosin 1α (TPM1) protein in rat remnant kidneys and in kidneys from IgA nephropathy patients. The increases in rat remnant kidneys were attenuated by the L-mimosine treatment. COL2A1 and TPM1 were confirmed to be new, direct targets of miR-29c. In conclusion, miR-29c, an antifibrotic microRNA, is upregulated by HIF-α activation. MiR-29c is downregulated in renal interstitial fibrosis in humans and rats and restored by activation of HIF-α that attenuates fibrosis.
Keywords: HIF; collagen type II α1; miR-29c; tropomyosin 1α; tubulointerstitial fibrosis.
Figures
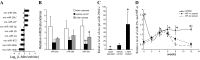


References
-
- Cao CC, Ding XQ, Ou ZL, Liu CF, Li P, Wang L, Zhu CF. In vivo transfection of NF-kappaB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides attenuate renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Kidney Int 65: 834–845, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Chevalier RL, Forbes MS, Thornhill BA. Ureteral obstruction as a model of renal interstitial fibrosis and obstructive nephropathy. Kidney Int 75: 1145–1152, 2009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

