Effects of balance training using a virtual-reality system in older fallers
- PMID: 23467506
- PMCID: PMC3588606
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S41453
Effects of balance training using a virtual-reality system in older fallers
Abstract
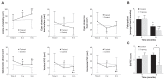
Poor balance is considered a challenging risk factor for falls in older adults. Therefore, innovative interventions for balance improvement in this population are greatly needed. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of a new virtual-reality system (the Balance Rehabilitation Unit [BRU]) on balance, falls, and fear of falling in a population of community-dwelling older subjects with a known history of falls. In this study, 60 community-dwelling older subjects were recruited after being diagnosed with poor balance at the Falls and Fractures Clinic, Nepean Hospital (Penrith, NSW, Australia). Subjects were randomly assigned to either the BRU-training or control groups. Both groups received the usual falls prevention care. The BRU-training group attended balance training (two sessions/week for 6 weeks) using an established protocol. Change in balance parameters was assessed in the BRU-training group at the end of their 6-week training program. Both groups were assessed 9 months after their initial assessment (month 0). Adherence to the BRU-training program was 97%. Balance parameters were significantly improved in the BRU-training group (P < 0.01). This effect was also associated with a significant reduction in falls and lower levels of fear of falling (P < 0.01). Some components of balance that were improved by BRU training showed a decline after 9 months post-training. In conclusion, BRU training is an effective and well-accepted intervention to improve balance, increase confidence, and prevent falls in the elderly.
Keywords: balance; elderly; falls; postural instability; virtual reality.
Figures


References
-
- Close JC, Lord SR. Fall assessment in older people. BMJ. 2011;343:d5153. - PubMed
-
- Nyman SR, Victor CR. Older people’s recruitment, sustained participation, and adherence to falls prevention interventions in institutional settings: a supplement to the Cochrane systematic review. Age Ageing. 2011;40(4):430–436. - PubMed
-
- Wetmore SJ, Eibling DE, Goebel JA, et al. Challenges and opportunities in managing the dizzy older adult. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011;144(5):651–656. - PubMed
-
- Muir SW, Montero-Odasso M. Effect of vitamin d supplementation on muscle strength, gait and balance in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(12):2291–2300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

