Resistance to Dutch elm disease reduces presence of xylem endophytic fungi in Elms (Ulmus spp.)
- PMID: 23468900
- PMCID: PMC3585289
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056987
Resistance to Dutch elm disease reduces presence of xylem endophytic fungi in Elms (Ulmus spp.)
Abstract
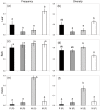
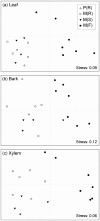
Efforts to introduce pathogen resistance into landscape tree species by breeding may have unintended consequences for fungal diversity. To address this issue, we compared the frequency and diversity of endophytic fungi and defensive phenolic metabolites in elm (Ulmus spp.) trees with genotypes known to differ in resistance to Dutch elm disease. Our results indicate that resistant U. minor and U. pumila genotypes exhibit a lower frequency and diversity of fungal endophytes in the xylem than susceptible U. minor genotypes. However, resistant and susceptible genotypes showed a similar frequency and diversity of endophytes in the leaves and bark. The resistant and susceptible genotypes could be discriminated on the basis of the phenolic profile of the xylem, but not on basis of phenolics in the leaves or bark. As the Dutch elm disease pathogen develops within xylem tissues, the defensive chemistry of resistant elm genotypes thus appears to be one of the factors that may limit colonization by both the pathogen and endophytes. We discuss a potential trade-off between the benefits of breeding resistance into tree species, versus concomitant losses of fungal endophytes and the ecosystem services they provide.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Fungal Assemblages in Northern Elms-Impacts of Host Identity and Health, Growth Environment, and Presence of Dutch Elm Disease.Microb Ecol. 2025 Jul 24;88(1):82. doi: 10.1007/s00248-025-02585-2. Microb Ecol. 2025. PMID: 40707845 Free PMC article.
-
Leaf trait dissimilarities between Dutch elm hybrids with a contrasting tolerance to Dutch elm disease.Ann Bot. 2013 Feb;111(2):215-27. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcs274. Epub 2012 Dec 21. Ann Bot. 2013. PMID: 23264236 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic distinction of Ulmus minor xylem tissues after inoculation with Ophiostoma novo-ulmi.Phytochemistry. 2005 Oct;66(20):2458-67. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2005.08.004. Epub 2005 Sep 19. Phytochemistry. 2005. PMID: 16176827
-
Complexities underlying the breeding and deployment of Dutch elm disease resistant elms.New For (Dordr). 2023;54(4):661-696. doi: 10.1007/s11056-021-09865-y. Epub 2021 Jul 28. New For (Dordr). 2023. PMID: 37361260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbe Profile: Xylella fastidiosa - a devastating agricultural pathogen with an endophytic lifestyle.Microbiology (Reading). 2021 Oct;167(10):001091. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001091. Microbiology (Reading). 2021. PMID: 34596503 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic variation along an altitudinal gradient in the Phytophthora infestans effector gene Pi02860.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 8;13:972928. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.972928. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36160230 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Methodological, Biotic and Abiotic Factors Influencing the Characterization of Xylem-Inhabiting Microbial Communities of Olive Trees.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 17;12(4):912. doi: 10.3390/plants12040912. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36840260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Massive sequencing of Ulmus minor's transcriptome provides new molecular tools for a genus under the constant threat of Dutch elm disease.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Jul 20;6:541. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00541. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26257751 Free PMC article.
-
Active Fungal Communities in Asymptomatic Eucalyptus grandis Stems Differ between a Susceptible and Resistant Clone.Microorganisms. 2019 Sep 20;7(10):375. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7100375. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31547186 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination of Elms against Dutch Elm Disease-Are the Associated Epiphytes and Endophytes Affected?J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Feb 24;9(3):297. doi: 10.3390/jof9030297. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McGuire KL, Treseder KK (2010) Microbial communities and their relevance for ecosystem models: Decomposition as a case study. Soil Biol Biochem 42: 529–535.
-
- Saikkonen K (2007) Forest structure and fungal endophytes. Fungal Biol Rev 21: 67–74.
-
- Sieber TN (2007) Endophytic fungi in forest trees: are they mutualists? Fungal Biol Rev 21: 75–89.
-
- Ahlholm J, Helander M, Elamo P, Saloniemi I, Neuvonen S, et al. (2002) Micro-fungi and invertebrate herbivores on birch trees: fungal mediated plant–herbivore interactions or responses to host quality? Ecol Lett 5: 648–655.
-
- Schulz B, Boyle C (2005) The endophytic continuum. Mycol Res 109: 661–686. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

