Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 peptides inhibit angiogenesis and choroidal neovascularization in mice
- PMID: 23469166
- PMCID: PMC3585964
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055667
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 peptides inhibit angiogenesis and choroidal neovascularization in mice
Abstract
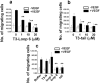
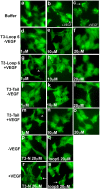
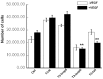
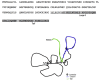
Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) while originally characterized as inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) have recently been shown to have a wide range of functions that are independent of their MMP inhibitory properties. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 (TIMP-3) is a potent inhibitor of VEGF-mediated angiogenesis and neovascularization through its ability to block the binding of VEGF to its receptor VEGFR-2. To identify and characterize the anti-angiogenic domain of TIMP-3, structure function analyses and synthetic peptide studies were performed using VEGF-mediated receptor binding, signaling, migration and proliferation. In addition, the ability of TIMP-3 peptides to inhibit CNV in a mouse model was evaluated. We demonstrate that the anti-angiogenic property resides in the COOH-terminal domain of TIMP-3 protein which can block the binding of VEGF specifically to its receptor VEGFR-2, but not to VEGFR-1 similar to the full-length wild-type protein. Synthetic peptides corresponding to putative loop 6 and tail region of TIMP-3 have anti-angiogenic properties as determined by inhibition of VEGF binding to VEGFR-2, VEGF-induced phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 and downstream signaling pathways as well as endothelial cell proliferation and migration in response to VEGF. In addition, we show that intravitreal administration of TIMP-3 peptide could inhibit the size of laser-induced choroidal neovascularization lesions in mice. Thus, we have identified TIMP-3 peptides to be efficient inhibitors of angiogenesis and have a potential to be used therapeutically in diseases with increased neovascularization.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Amour A, Knight CG, Webster A, Slocombe PM, Stephens PE, et al. (2000) The in vitro activity of ADAM-10 is inhibited by TIMP-1 and TIMP-3. FEBS Lett 473: 275–279. - PubMed
-
- Amour A, Slocombe PM, Webster A, Butler M, Knight CG, et al. (1998) TNF-alpha converting enzyme (TACE) is inhibited by TIMP-3. FEBS Lett 435: 39–44. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto G, Aoki T, Nakamura H, Tanzawa K, Okada Y (2001) Inhibition of ADAMTS4 (aggrecanase-1) by tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMP-1, 2, 3 and 4). FEBS Lett 494: 192–195. - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen J, Visse R, Sorensen HP, Enghild JJ, Brew K, et al. (2008) Catalytic properties of ADAM12 and its domain deletion mutants. Biochemistry 47: 537–547. - PubMed
-
- Kashiwagi M, Tortorella M, Nagase H, Brew K (2001) TIMP-3 is a potent inhibitor of aggrecanase 1 (ADAM-TS4) and aggrecanase 2 (ADAM-TS5). J Biol Chem 276: 12501–12504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

