TAp73β-mediated suppression of cell migration requires p57Kip2 control of actin cytoskeleton dynamics
- PMID: 23470527
- PMCID: PMC3712574
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.833
TAp73β-mediated suppression of cell migration requires p57Kip2 control of actin cytoskeleton dynamics
Abstract
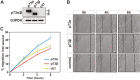
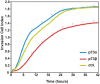
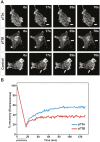
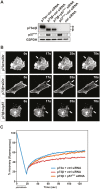
The TP73 gene, a member of the p53 family, due to the use of different promoters and alternative splicing, is transcribed into different isoforms with contrasting attributes and which contribute to its functional diversity. Considerable efforts are made to identify the functional diversity of the p73 splicing variants during tumorigenesis. TAp73α and TAp73β isoforms have been shown to differentially regulate cell cycle progression, differentiation and apoptosis. Interestingly, a particular increase in expression of the TAp73 isoform, in favor of the α splicing variant, has been reported in multiple tumour types. Here, we report a distinctive role for TAp73β isoform in the control of cell migration and invasion. In fact, TAp73β- dependent induction of p57(Kip2) expression accounted for inhibitory effects on the actin cytoskeleton dynamics and thereby cancer cell motility. In contrast, TAp73α is not able to induce p57(Kip2) expression, and exhibits a positive effect on actin cytoskeleton dynamics as well as cell migration and invasion. In conclusion, the inhibitory effect on cell migration and invasion of TAp73β would qualify this distinct p73 isoform as tumor suppressor gene. In contrast, the promoting effect of TAp73α on cell motility and invasion strengthens the potential oncogenic activities of this p73 isoform.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Kaghad M, Bonnet H, Yang A, Creancier L, Biscan JC, Valent A, Minty A, Chalon P, Lelias JM, Dumont X, Ferrara P, McKeon F, Caput D. Monoallelically expressed gene related to p53 at 1p36, a region frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other human cancers. Cell. 1997;90(4):809–819. - PubMed
-
- Jost CA, Marin MC, Kaelin WG., Jr p73 is a simian [correction of human] p53-related protein that can induce apoptosis. Nature. 1997;389(6647):191–194. - PubMed
-
- De Laurenzi V, Raschella G, Barcaroli D, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Ranalli M, Catani MV, Tanno B, Costanzo A, Levrero M, Melino G. Induction of neuronal differentiation by p73 in a neuroblastoma cell line. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(20):15226–15231. - PubMed
-
- Melino G, De Laurenzi V, Vousden KH. p73: Friend or foe in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(8):605–615. - PubMed
-
- Stiewe T, Zimmermann S, Frilling A, Esche H, Putzer BM. Transactivation-deficient DeltaTA-p73 acts as an oncogene. Cancer Res. 2002;62(13):3598–3602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

