SPLUNC1 regulates cell progression and apoptosis through the miR-141-PTEN/p27 pathway, but is hindered by LMP1
- PMID: 23472073
- PMCID: PMC3589440
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056929
SPLUNC1 regulates cell progression and apoptosis through the miR-141-PTEN/p27 pathway, but is hindered by LMP1
Abstract
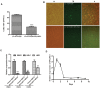
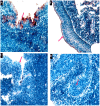
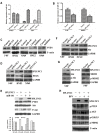
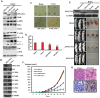
Little is known about the role of the host defensive protein short palate, lung and nasal epithelium clone 1 (SPLUNC1) in the carcinogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Here we report that SPLUNC1 plays a role at a very early stage of NPC carcinogenesis. SPLUNC1 regulates NPC cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis through miR-141, which in turn regulates PTEN and p27 expression. This signaling axis is negatively regulated by the EBV-coded gene LMP1. Therefore we propose that SPLUNC1 suppresses NPC tumor formation and its inhibition by LMP1 provides a route for NPC tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Xiong W, Zeng ZY, Xia JH, Xia K, Shen SR, et al. (2004) A susceptibility locus at chromosome 3p21 linked to familial nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res 64: 1972–1974. - PubMed
-
- Zeng Z, Zhou Y, Zhang W, Li X, Xiong W, et al. (2006) Family-based association analysis validates chromosome 3p21 as a putative nasopharyngeal carcinoma susceptibility locus. Genet Med 8: 156–160. - PubMed
-
- Zeng Z, Huang H, Zhang W, Xiang B, Zhou M, et al. (2011) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: advances in genomics and molecular genetics. Sci China Life Sci 54: 966–975. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

