The AMPK family member Snf1 protects Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells upon glutathione oxidation
- PMID: 23472170
- PMCID: PMC3589272
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058283
The AMPK family member Snf1 protects Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells upon glutathione oxidation
Abstract
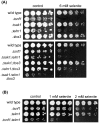
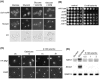
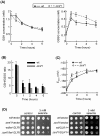
The AMPK/Snf1 kinase has a central role in carbon metabolism homeostasis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In this study, we show that Snf1 activity, which requires phosphorylation of the Thr210 residue, is needed for protection against selenite toxicity. Such protection involves the Elm1 kinase, which acts upstream of Snf1 to activate it. Basal Snf1 activity is sufficient for the defense against selenite, although Snf1 Thr210 phosphorylation levels become increased at advanced treatment times, probably by inhibition of the Snf1 dephosphorylation function of the Reg1 phosphatase. Contrary to glucose deprivation, Snf1 remains cytosolic during selenite treatment, and the protective function of the kinase does not require its known nuclear effectors. Upon selenite treatment, a null snf1 mutant displays higher levels of oxidized versus reduced glutathione compared to wild type cells, and its hypersensitivity to the agent is rescued by overexpression of the glutathione reductase gene GLR1. In the presence of agents such as diethyl maleate or diamide, which cause alterations in glutathione redox homeostasis by increasing the levels of oxidized glutathione, yeast cells also require Snf1 in an Elm1-dependent manner for growth. These observations demonstrate a role of Snf1 to protect yeast cells in situations where glutathione-dependent redox homeostasis is altered to a more oxidant intracellular environment and associates AMPK to responses against oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Sanz P (2003) Snf1 protein kinase: a key player in the response to cellular stress in yeast. Biochem Soc Trans 31: 178–181. - PubMed
-
- McCartney RR, Schmidt MC (2001) Regulation of Snf1 kinase. Activation requires phosphorylation of threonine 210 by an upstream kinase as well as a distinct step mediated by the Snf4 subunit. J Biol Chem 276: 36460–36466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

