Orientations and proximities of the extracellular ends of transmembrane helices S0 and S4 in open and closed BK potassium channels
- PMID: 23472181
- PMCID: PMC3589268
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058335
Orientations and proximities of the extracellular ends of transmembrane helices S0 and S4 in open and closed BK potassium channels
Abstract
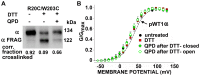
The large-conductance potassium channel (BK) α subunit contains a transmembrane (TM) helix S0 preceding the canonical TM helices S1 through S6. S0 lies between S4 and the TM2 helix of the regulatory β1 subunit. Pairs of Cys were substituted in the first helical turns in the membrane of BK α S0 and S4 and in β1 TM2. One such pair, W22C in S0 and W203C in S4, was 95% crosslinked endogenously. Under voltage-clamp conditions in outside-out patches, this crosslink was reduced by DTT and reoxidized by a membrane-impermeant bis-quaternary ammonium derivative of diamide. The rate constants for this reoxidation were not significantly different in the open and closed states of the channel. Thus, these two residues are approximately equally close in the two states. In addition, 90% crosslinking of a second pair, R20C in S0 and W203C in S4, had no effect on the V50 for opening. Taken together, these findings indicate that separation between residues at the extracellular ends of S0 and S4 is not required for voltage-sensor activation. On the contrary, even though W22C and W203C were equally likely to form a disulfide in the activated and deactivated states, relative immobilization by crosslinking of these two residues favored the activated state. Furthermore, the efficiency of recrosslinking of W22C and W203C on the cell surface was greater in the presence of the β1 subunit than in its absence, consistent with β1 acting through S0 to stabilize its immobilization relative to α S4.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Positions of the cytoplasmic end of BK α S0 helix relative to S1-S6 and of β1 TM1 and TM2 relative to S0-S6.J Gen Physiol. 2015 Mar;145(3):185-99. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201411337. Epub 2015 Feb 9. J Gen Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25667410 Free PMC article.
-
Locations of the beta1 transmembrane helices in the BK potassium channel.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Aug 5;105(31):10727-32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805212105. Epub 2008 Jul 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18669652 Free PMC article.
-
Position and role of the BK channel alpha subunit S0 helix inferred from disulfide crosslinking.J Gen Physiol. 2008 Jun;131(6):537-48. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200809968. Epub 2008 May 12. J Gen Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18474637 Free PMC article.
-
Large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BK) channel: activation by Ca2+ and voltage.Biol Res. 2006;39(3):385-401. doi: 10.4067/s0716-97602006000300003. Epub 2006 Nov 7. Biol Res. 2006. PMID: 17106573 Review.
-
Emerging issues of connexin channels: biophysics fills the gap.Q Rev Biophys. 2001 Aug;34(3):325-472. doi: 10.1017/s0033583501003705. Q Rev Biophys. 2001. PMID: 11838236 Review.
Cited by
-
Positions of the cytoplasmic end of BK α S0 helix relative to S1-S6 and of β1 TM1 and TM2 relative to S0-S6.J Gen Physiol. 2015 Mar;145(3):185-99. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201411337. Epub 2015 Feb 9. J Gen Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25667410 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism underlying β1 regulation in voltage- and calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 14;112(15):4809-14. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504378112. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25825713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marty A (1981) Ca-dependent K channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes. Nature 291: 497–500. - PubMed
-
- Pallotta BS, Magleby KL, Barrett JN (1981) Single channel recordings of Ca2+-activated K+ currents in rat muscle cell culture. Nature 293: 471–474. - PubMed
-
- Adelman JP, Shen KZ, Kavanaugh MP, Warren RA, Wu YN, et al. (1992) Calcium-activated potassium channels expressed from cloned complementary DNAs. Neuron 9: 209–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

