A novel arrangement of Cys residues in a paralytic peptide of Conus cancellatus (jr. syn.: Conus austini), a worm-hunting snail from the Gulf of Mexico
- PMID: 23474143
- PMCID: PMC3677226
- DOI: 10.1016/j.peptides.2013.02.016
A novel arrangement of Cys residues in a paralytic peptide of Conus cancellatus (jr. syn.: Conus austini), a worm-hunting snail from the Gulf of Mexico
Abstract
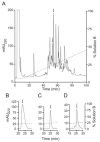
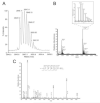
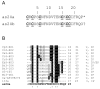
The present study details the purification, the amino acid sequence determination, and a preliminary characterization of the biological effects in mice of a new conotoxin from the venom of Conus cancellatus (jr. syn.: Conus austini), a worm-hunting cone snail collected in the western Gulf of Mexico (Mexico). The 23-amino acid peptide, called as25a, is characterized by the sequence pattern CX1CX2CX8CX1CCX5, which is, for conotoxins, a new arrangement of six cysteines (framework XXV) that form three disulfide bridges. The primary structure (CKCPSCNFNDVTENCKCCIFRQP*; *, amidated C-terminus; calculated monoisotopic mass, 2644.09Da) was established by automated Edman degradation after reduction and alkylation, and MALDI-TOF and ESI mass spectrometry (monoisotopic mass, 2644.12/2644.08Da). Upon intracranial injection in mice, the purified peptide provokes paralysis of the hind limbs and death with a dose of 240 pmol (~0.635 μg, ~24.9 ng/g). In addition, a post-translational variant of this peptide (as25b) was identified and determined to contain two hydroxyproline residues. These peptides may represent a novel conotoxin gene superfamily.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Alonso D, Khalil Z, Satkunanthan N, Livett BG. Drugs from the sea: conotoxins as drugs leads for neurophatic pain and other neurological conditions. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2003;3:785–7. - PubMed
-
- Anderson PAV, Greenberg RM. Phylogeny of ion channels: clues to structure and function. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 2001;129:17–28. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

