The minimal clinically important difference after simple decompression for ulnar neuropathy at the elbow
- PMID: 23474160
- PMCID: PMC3617491
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2013.01.022
The minimal clinically important difference after simple decompression for ulnar neuropathy at the elbow
Abstract
Purpose: Establishing minimally clinically important difference (MCID) for patient-reported outcomes questionnaires is an important component of outcomes research to understand treatment effectiveness from the patient's perspective. For patients with ulnar neuropathy at the elbow (UNE), these assessments are vital to examine how much change in the questionnaire scores equate to patient satisfaction.
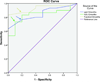
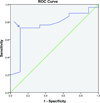
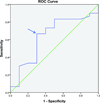
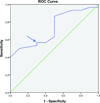
Methods: We calculated the change in scores of Michigan Hand Outcomes Questionnaire (MHQ), Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) questionnaire, and Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire (CTQ) from preoperative to 3, 6, and 12 months after ulnar nerve simple decompression procedure. We used the anchor-based approach of receiver operating characteristic curves to determine the MCID.
Results: On average, MCID of 10, 12, and 7 points were identified for pain, function, and activities of daily living domains of the MHQ. Similarly, DASH, CTQ-symptom severity scale, and CTQ-function severity scale had an average MCID of 7, 0.7, and 0.3, points respectively. At the 3, 6, and 12 months' time points, an MCID of 9, 8, and 13 points for pain; 12, 12, and 12 points for function; and 6, 8, and 6 points for activities of daily living domains of the MHQ were identified; similarly an MCID of 8, 7, and 7 points for DASH; 0.4, 0.7, and 0.7 points for CTQ-symptom severity scale; and 0.3, 0.3, and 0.4 points for CTQ-function severity scale were established.
Conclusions: The smaller MCIDs of MHQ, DASH, and even smaller MCIDs of CTQ found in our study indicate that a small change in the scores identified satisfied patients. Simple decompression surgery for UNE produced patient satisfaction with only a small change in their questionnaire scores. The implications of this finding are that simple decompression surgery for UNE is a highly effective procedure and that the outcomes questionnaires used are highly responsive, which minimizes sample size requirements for future research studies relating to UNE.
Type of study/level of evidence: Therapeutic II.
Copyright © 2013 American Society for Surgery of the Hand. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Pynsent PB. Choosing an outcome measure. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83(6):792–794. - PubMed
-
- Ozyurekoglu T, McCabe SJ, Goldsmith LJ, LaJoie AS. The minimal clinically important difference of the Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Symptom Severity Scale. J Hand Surg Am. 2006;31(5):733–738. discussion 739–740. - PubMed
-
- Dawson J, Doll H, Boller I, Fitzpatrick R, Little C, Rees J, et al. Comparative responsiveness and minimal change for the Oxford Elbow Score following surgery. Qual Life Res. 2008;17(10):1257–1267. - PubMed
-
- Mondelli M, Padua L, Giannini F, Bibbo G, Aprile I, Rossi S. A self-administered questionnaire of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. Neurol Sci. 2006;27(6):402–411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

