Stiffened lipid platforms at molecular force foci
- PMID: 23476066
- PMCID: PMC3612676
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1302018110
Stiffened lipid platforms at molecular force foci
Abstract
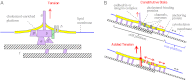
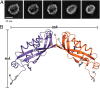
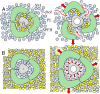
How mechanical forces are sensed remains largely mysterious. The forces that gate prokaryotic and several eukaryotic channels were found to come from the lipid membrane. Our survey of animal cells found that membrane force foci all have cholesterol-gathering proteins and are reinforced with cholesterol. This result is evident in overt force sensors at the tips of stereocilia for vertebrate hearing and the touch receptor of Caenorhabditis elegans and mammalian neurons. For less specialized cells, cadherins sustain the force between neighboring cells and integrins between cells and matrix. These tension bearers also pass through and bind to a cholesterol-enriched platform before anchoring to cytoskeleton through other proteins. Cholesterol, in alliance with sphingomyelin and specialized proteins, enforces a more ordered structure in the bilayer. Such a stiffened platform can suppress mechanical noise, redirect, rescale, and confine force. We speculate that such platforms may be dynamic. The applied force may allow disordered-phase lipids to enter the platform-staging channel opening in the thinner mobile neighborhood. The platform may also contain specialized protein/lipid subdomains enclosing mechanosensitive channels to open with localized tension. Such a dynamic stage can mechanically operate structurally disparate channels or enzymes without having to tie them directly to cadherin, integrin, or other protein tethers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Martinac B, Adler J, Kung C. Mechanosensitive ion channels of E. coli activated by amphipaths. Nature. 1990;348(6298):261–263. - PubMed
-
- Sukharev SI, Blount P, Martinac B, Kung C. Mechanosensitive channels of Escherichia coli: The MscL gene, protein, and activities. Annu Rev Physiol. 1997;59:633–657. - PubMed
-
- Sukharev SI, Blount P, Martinac B, Blattner FR, Kung C. A large-conductance mechanosensitive channel in E. coli encoded by mscL alone. Nature. 1994;368(6468):265–268. - PubMed
-
- Anishkin A, Kung C. Microbial mechanosensation. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2005;15(4):397–405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

